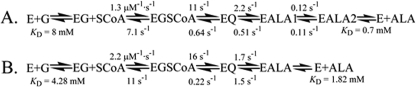FIGURE 6.
The simulated kinetic mechanisms of the wild-type ALAS-catalyzed (A) and SS2 variant-catalyzed (B) reactions. Transition from an internal aldimine between the PLP cofactor and lysine 313 to an external aldimine with glycine is the first step. Binding of succinyl-CoA occurs next, which is followed by formation of the quinonoid intermediate and protonation of the quinonoid intermediate to yield an aldimine bound molecule of ALA. Finally, the release of ALA completes the reaction. E, wild-type ALAS or SS2 variant; G, glycine; EG, enzyme-glycine complex; SCoA, succinyl-CoA; EGSCoA, ALAS-glycine-succinyl-CoA complex; EQ, observable quinonoid intermediate; EALA, ALAS-ALA external aldimine; EALA1, ALAS-ALA external aldimine with active site loop closed; EALA2, ALAS-ALA external aldimine with active site loop open. (The rate and dissociation constants for the wild-type ALAS-catalyzed reaction were previously reported (10).)