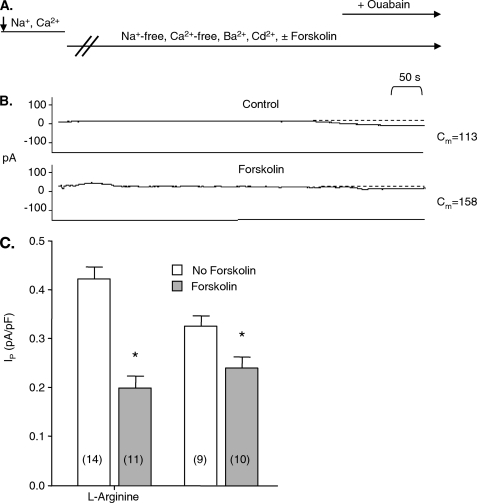
FIGURE 3.
Effect of forskolin on Na+-K+ pump current in myocytes. Panel A shows the timing of changes in the composition of superfusates. The arrow on the left side of the panel indicates establishment of the whole-cell configuration and, hence, perfusion of the intracellular compartment with pipette solution. The switch from a Ca2+-containing, forskolin-free solution in the tissue bath to a nominally Ca2+-free solution containing Ba2+, Cd2+, and forskolin and the switch to a solution also containing ouabain (the arrow on the right side of the panel) are shown. Panel B shows examples of holding currents. Large changes in the currents that occur the first 1–2 min after the switch to Na+- and Ca2+-free Ba2+- and Cd2+-containing superfusate before currents stabilize are not shown. Stable holding currents before exposure of myocytes to ouabain are important for the measurement of Ip. Stability of the currents as well as the ouabain-induced shift in them was identified from the read-out of an electronic cursor. Cm indicates membrane capacitance in picofarads (pF). Panel C shows the mean Ip normalized for membrane capacitance. The pipette solution contained l-arginine where indicated. The numbers of myocytes in each group are indicated in parentheses. The asterisk indicates a significant difference between the means of Ip.