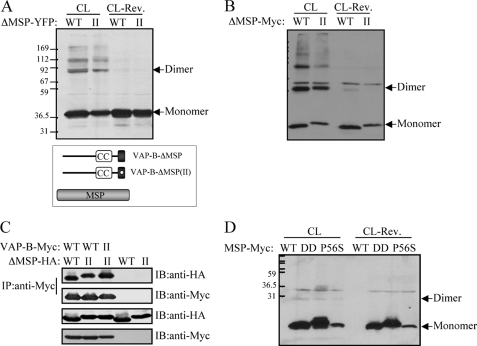
FIGURE 2.
The MSP domain does not contribute to VAP-B oligomerization. The indicated VAP-B mutants lacking the MSP domain (ΔMSP) of either the WT or the VAP-B(II) mutant were expressed HEK293 cells. Their self-assembly was assessed following cross-linking by Western blotting using anti-GFP (A) or anti-Myc (B) antibodies. The position of the monomer and the dimer is marked by an arrow. C, the indicated HA-tagged ΔMSP mutants were expressed either alone or together with the indicated Myc-tagged VAP-B proteins, and their interaction was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation studies using anti-Myc antibody for immunoprecipitation and anti-HA antibody for immunoblotting. D, the Myc-tagged MSP domains of the wild-type VAP-B, the K87/M89D (DD) double mutant, or the P56S mutant were expressed in HEK293 cells. Their self-assembly was assessed following cross-linking (CL) by Western blotting using anti-Myc antibody. Cross-linker cleavage: CL-Rev. Note that the expression level of the MSP-P56S mutant is relatively low, implying that it is not as stable as the other mutants. The position of the monomer and the dimer is marked by an arrow. Positions of prestained molecular mass markers, in kDa, are indicated on the left.