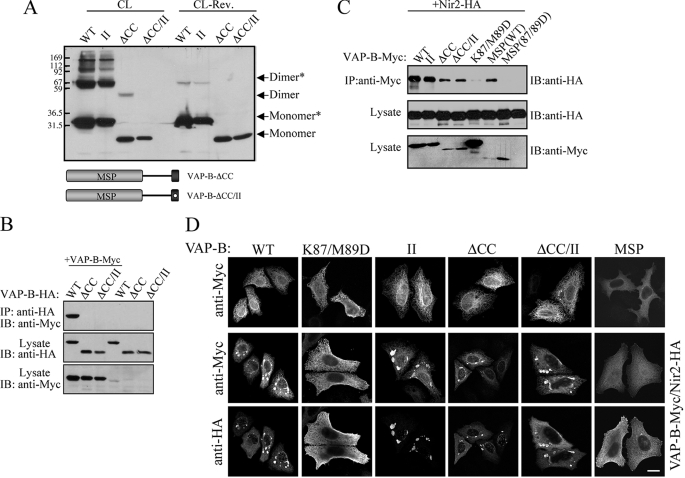
FIGURE 3.
The coiled-coil domain is critical for VAP-B oligomerization. Deletion of the coiled-coil (ΔCC) domain markedly reduces VAP-B oligomerization and together with the II mutant apparently abolishes VAP-B homo- (A) and hetero-dimerization (B) as determined by cross-linking experiments (A) and coimmunoprecipitation studies (B), respectively. C, deletion of the coiled-coil domain has no effect on Nir2 binding. The indicated Myc-tagged VAP-B proteins were co-expressed with HA-tagged Nir2, and their association was assessed by immunoprecipitation using anti-Myc antibody following by immunoblotting using anti-HA antibody. D, the indicated Myc-tagged VAP-B proteins were expressed in HeLa cells either alone or together with HA-tagged Nir2. The localization of the indicated proteins was determined by indirect immunofluorescence analysis. Representative confocal images demonstrating the formation of stacked ER-membrane arrays upon co-expression with Nir2 are shown in the lower panels. Scale bar, 10 μm.