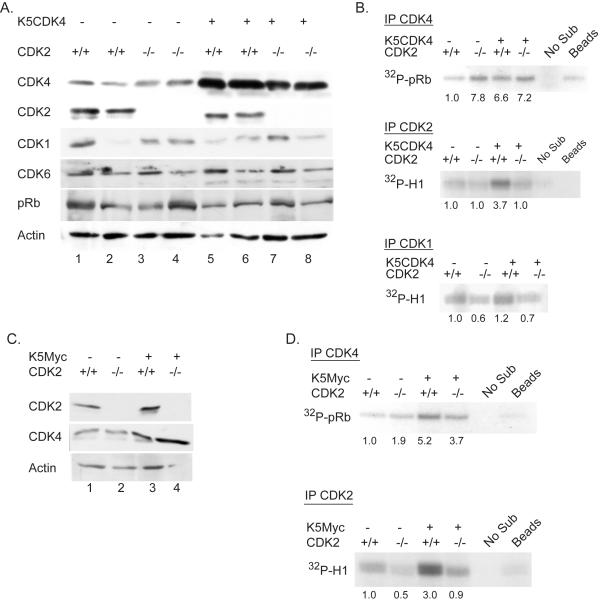
Figure 2.
Biochemical analysis of K5CDK4/CDK2−/− and K5Myc/CDK2−/− mice epidermis. (A) Immunoblots analysis of epidermal protein lysates from age matched wild type (1-2), CDK2−/− (3-4), K5CDK4 (5-6) and K5CDK4/CDK2−/− (7-8) mice. Antibodies against CDKs and pRb are indicated on the left column. Immunoblot for actin used as loading control. (B) CDK kinase assays of epidermal protein lysates from age matched wild type, CDK2−/−, K5CDK4 and K5CDK4/CDK2−/− mice were carried out with antibodies against CDK4 (IP CDK4), CDK2 (IP CDK2) and CDK1 (IP CDK1) using pRb and histone H1 peptides as substrates. Fold increase in CDK kinase activities gauged in comparison to wild type activity. (C) Immunoblots analysis of wild type (1), CDK2−/− (2), K5-Myc (3) and K5-Myc/CDK2−/− (4) epidermal lysates for CDK2, CDK4 and actin as loading control. (D) CDK kinase assay of epidermal lysates from age matched wild type, CDK2−/−, K5Myc and K5Myc/CDK2−/− mice were carried out with antibodies against CDK4 (IP CDK4) and CDK2 (IP CDK2) using pRb and histone H1 peptides as substrates, respectively. Fold increase in CDK kinase activities gauged in comparison to wild type activity. Control “Beads”, immunoprecipitation using normal rabbit IgG and K5CDK4 (B) or K5Myc (D) lysates. Control “No Sub”, kinase reaction without pRb or H1 recombinant protein substrates.