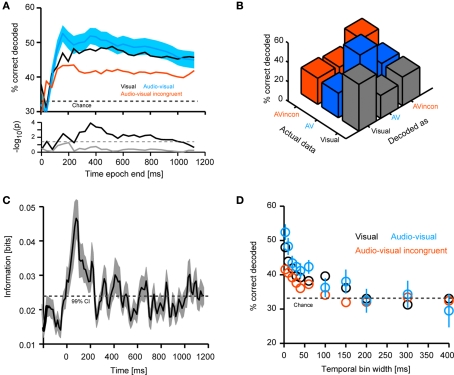
Figure 3.
Decoding of different stimulus modality combinations. (A) Performance in decoding the different stimulus conditions (visual, congruent and incongruent audio-visual). For decoding the full time course of the response sampled at 20 ms was considered. The graphs display decoding performance as a function of the response interval considered, which started at stimulus onset and terminated at the corresponding value on the x-axis. Lines denote the mean across units (n = 61), blue area indicates the standard error for the congruent condition. Chance level is 33%. The lower panel displays the p-values (on a negative logarithmic axis) of point-wise t-tests between congruent and incongruent bimodal conditions (black) and visual and congruent bimodal conditions (gray). The dashed line indicates a critical p-value of 0.05 corrected for false discovery rate (for the black trace). (B) Confusion matrix of the decoding performance (considering the first 800 ms of the response). Left axis indicates the to-be-decoded condition, right axis indicates the decoded condition. Correctly decoded trials fall on the diagonal. (C) Shannon information between response amplitude and modality condition. Black line denotes the mean across units, shaded area the standard error. Information was computed using sliding windows and the 99% confidence interval (CI) was obtained from a bootstrap test. (D) Performance in decoding the different stimulus conditions (considering the first 800 ms of the response) as a function of the temporal resolution (bin width) at which the response is sampled. Circles denote the mean across units, bars the standard error.