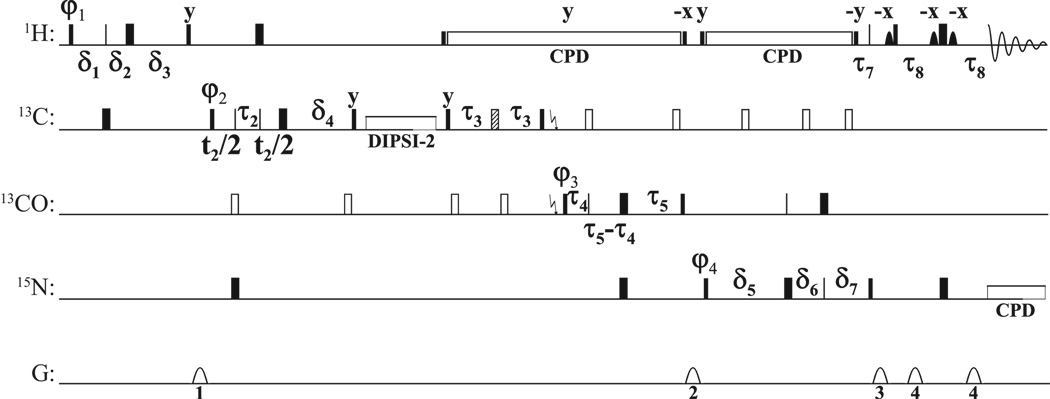
Figure 1.
For 1H and 15N, narrow and wide rectangles represent 90° and 180° pulses (for hard pulses at 28.3 and 6.25 kHz) respectively. For 13C, solid narrow and wide rectangles denote on-resonance Q5 and Q3 pulses[27], while open rectangles represent pulses that are applied off-resonance by means of a phaseramp.[28] The hatched pulse represents a Cα-selective Q3 pulse. For 13C, every second 90° pulse is a time-reversed Q5. The pulse lengths are 274 µs for Q5/time-reversed Q5 pulses at a RF field strength of 16.7 kHz, 170 µs at 19.4 kHz for 180° pulses applied to all aliphatic carbons, and 667 µs at 4.95 kHz for the Cα-selective Q3 pulse. Solid shapes are selective pulses applied to the water magnetization (Sinc1 shape of 1 ms length at 425 Hz). The 1H decoupling (DIPSI2[29] at 6.25 kHz) is flanked by 90° pulses given at the same power level. A DIPSI2[29] spinlock is applied for 11.5 ms at 10 kHz to achieve the CC TOCSY transfer. A garp4 supercycle is used for 15N decoupling during acquisition (1.39 kHz).[30] The delays are: τ1 = 1/(41JCH) (1.7 ms), τ2 = 1/(61JCH) (1.1 ms), τ3 = 1/(41JCαCO) (4.5 ms), τ4 = 1/(41JCαCO) (4.4 ms), τ5 = 1/(41JCON) (12.4 ms), τ6 = τ5, τ7 = (1/(21JNH) (5.5 ms), τ8 = 2.3ms 1/(41JNH) (2.3 ms; reduced to partially compensate for relaxation losses),ε1 = τp (13C 180°) + initial setting of (1−κ1)t1/2, ε2 = τp (1H 180°) + initial setting of t2, ε3 = τp (13C 180°) + initial setting of (1−κ3)t3/2, δ1=τ1+t1/2, δ2=(1−κ1)t1/2, δ3=τ1−κ1t1/2+ε1, δ4=τ2+ε2, δ5=τ6−κ3t3/2+ε3, δ6=(1−κ3)t3/2, δ7=τ6+t3/2. All pulses are along x except otherwise noted. The phase cycles are φ1 = x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, −x, −x, −x, −x, −x, −x, −x, −x; φ2 = x, x, −x, −x; φ3 = x, x, x, x, −x, −x, −x, −x; φ4 = x, −x; φreceive) = x, −x, −x, x, −x, x, x, −x, −x, x, x, −x, x, −x, −x, x. Gradients (1 ms) are sine-shaped with an amplitude of 25, 20, 30 and 15 G/cm respectively. Labeling of chemical shifts is performed in a semi-constant time fashion.[31; 32; 33] Phase sensitive spectra are obtained using the States-TPPI method[34] by either incrementing τ1, τ2 or decrementing τ4 respectively in different experiments. Water suppression was achieved by using a soft pulse WATERGATE scheme.[35; 36]