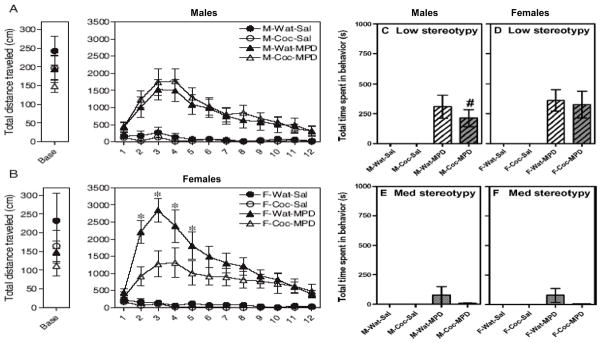
Figure 1.
Locomotor activity and stereotyped behavior after acute injection of either saline or methylphenidate (MPD). Panel A shows adolescent male rats and Panel B shows adolescent female rats that were exposed to prenatal cocaine or water (controls) and then challenged with saline or MPD. Baseline activity was collected during 20 min and illustrated as an average for that period. Panels C and D show Low intensity stereotypy (repeated head movements with locomotion) in the same male and female rats. Panels E and F show Medium intensity stereotypy (more intense repeated head movements with or without locomotion) in the same male and female rats. White bars illustrate water pretreated rats and gray bars represent cocaine pre-treated rats. N= 10–12 rats per group. Bars represent sem and * represents significantly different from all other groups. # represents significantly different from prenatal control males that also received MPD. Modified from Torres-Reveron & Dow-Edwards Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 2006; 28: 165–172.