Fig. 2.
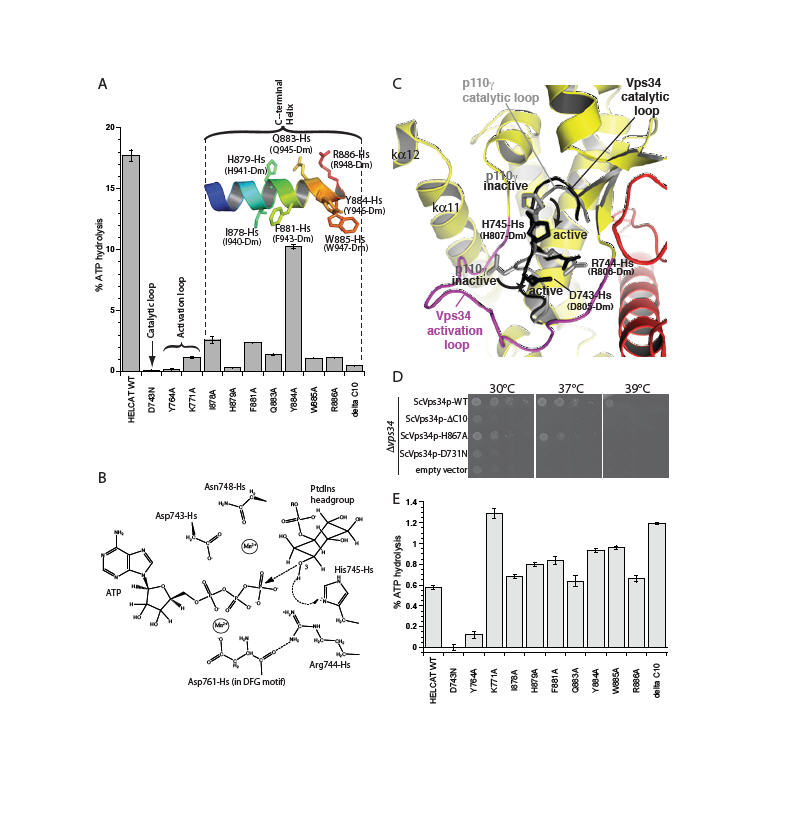
Essential structural elements for Vps34 catalysis. (A) The catalytic loop, the activation loop and the amphipathic C-terminal helix are critical for catalysis on PtdIns:PS vesicles. (B) Proposed catalytic mechanism of Vps34. (C) A close-up view of the proposed movements of catalytic loop residues His745-Hs and Asp743-Hs between the inactive and active conformations represented by the p110γ (grey) and DmVps34 crystal structure (black), respectively. (D) The ability of a yeast Vps34p-expressing plasmid to complement the growth defect of a Δvps34 yeast strain at elevated temperatures is impaired by deletion of the C-terminal helix (Vps34p ΔC10), a point mutation in this helix (ScH867A) or a mutation in the catalytic loop (ScD731N). (E) Basal ATPase activities in the absence of vesicles.
