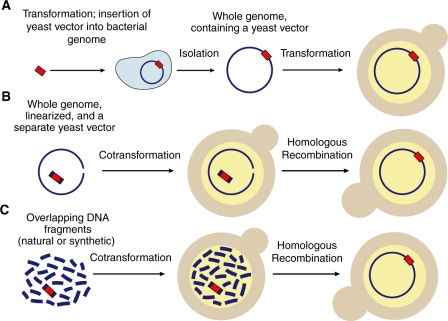
Figure 1.
Three methods for cloning mycoplasma genomes in yeast. In order to be propagated by yeast (tan, with yellow nucleus) upon transformation, the bacterial genome (blue circle) must contain several yeast sequences (vector, red bar). (A) These can be incorporated into the bacterial genome by transformation of the bacterium (light blue). (B) Alternatively, they can be inserted by cotransformation of yeast with the vector and the bacterial genome. In this case the two must share overlapping sequences, so that yeast can combine them by homologous recombination. (C) The bacterial genome can also be cloned by assembling multiple overlapping fragments.