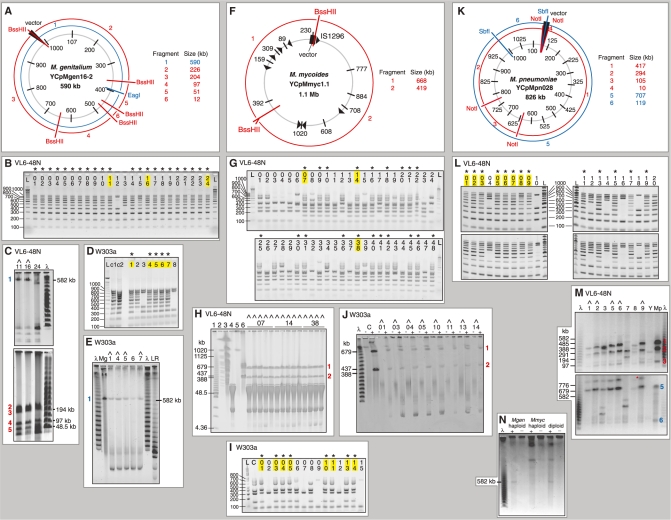
Figure 3.
Gel analysis of whole mycoplasma genome clones in yeast. The host yeast strain of each set of clones is marked above the gel. Clones were first assayed for completeness by multiplex PCR (B, D, G, I, L). Complete clones are marked with an asterisk, and those selected for sizing by restriction digestion and gel electrophoresis (C, E, H, J, M) are highlighted in yellow. Clones judged to be the correct size are marked with a caret. L is a 100-bp ladder (Invitrogen), λ is a lambda ladder (NEB) and LR is the Low Range PFG ladder (NEB); selected bands are labeled. (A) Map of the M. genitalium YCpMgen16-2 genome. The location of the yeast vector insertion is marked. Bars indicate position and numbers indicate size of PCR amplicons. Restriction fragments are numbered and their sizes given in red or blue. (B) Multiplex PCR analysis of 24 yeast clones derived from YCpMgen16-2, using primers shown in (A). (C) Selected clones assayed as correct in (B) digested with EagI (top gel) or BssHII (bottom gel) and separated by field inversion gel electrophoresis (FIGE). Yeast chromosomal DNA was removed prior to this analysis by digestion with FseI, RsrII, and AsiSI, followed by constant voltage electrophoresis (these enzymes do not have recognition sites in YCpMgen16-2 and large circular DNA molecules remained in the agarose plugs under these conditions). (D) Multiplex PCR analysis of eight yeast clones derived from YCpMgen16-2, using primers shown in (A). sMgTARBAC37 (c1) (16) and M. genitalium (c2) DNAs were used as positive controls. (E) All clones assayed as correct in (D) linearized with EagI and separated by clamped homogenous electric field (CHEF). Before digestion, clones were pre-electrophoresed at constant voltage to remove linear yeast chromosomes. ‘Mg’ indicates NotI-digested 592-kb sMgTARBAC37 (16). Clone 6 contains a faint extra band of ∼300 kb. (F) Map of the M. mycoides YCpMmyc1.1 genome. The location of the yeast vector insertion is marked. Arrowheads represent IS1296 elements. Bars indicate position and numbers indicate size of PCR amplicons. Restriction fragments are numbered and their sizes given in red. (G) Multiplex PCR analysis of 48 yeast clones derived from YCpMmyc1.1, using primers shown in (F). An additional amplicon of 464 bp, not shown in (F), acted as a positive control by amplifying yeast rDNA. (H) Selected yeast clones assayed as correct in (G) digested with BssHII and separated by CHEF. The parent clone (far left in each set) and 3–4 subclones of each were analyzed. Markers and controls are: (1) Low Range PFG Marker (NEB); (2) S. cerevisiae marker (Bio-Rad); VL6-48N (3) undigested and (4) BssHII-digested; and YCpMmyc1.1 (5) undigested and (6) BssHII-digested. (I) Multiplex PCR analysis of 15 yeast clones derived from YCpMmyc1.1, using primers shown in (F). (J) All clones assayed as correct in (I) pre-electrophoresed at constant voltage to remove linear yeast chromosomes, then left undigested (−) or digested (+) with BssHII and separated by CHEF. ‘C’ indicates YCpMmyc1.1 DNA isolated from M. mycoides used as a positive control. (K) Map of the M. pneumoniae YCpMpn028 genome. The location of the yeast vector insertion is marked. Bars indicate position and numbers indicate size of PCR amplicons. Restriction fragments are numbered and their sizes given in red or blue. (L) Multiplex PCR analysis of 20 yeast clones derived from YCpMpn028, using primers shown in (K). (M) Selected clones assayed as correct in (L) pre-electrophoresed at constant voltage, then digested with NotI (top gel) or SbfI (bottom gel) and separated by CHEF. Host yeast strain VL6-48N is labeled ‘Y’ and M. pneumoniae DNA transformed into yeast is labeled ‘Mp’. A red asterisk marks incomplete digestion (linearization) of the yeast clone. (N) A haploid yeast strain containing an M. genitalium genome and a haploid yeast strain containing an M. mycoides genome are compared to a diploid yeast clone containing the two mycoplasma genomes. Clones were pre-electrophoresed at constant voltage, then left unheated (−) or incubated at 55°C for 1 h for linearization (+). The genomes are too large to move into the gel as circles; they must be linearized to migrate.