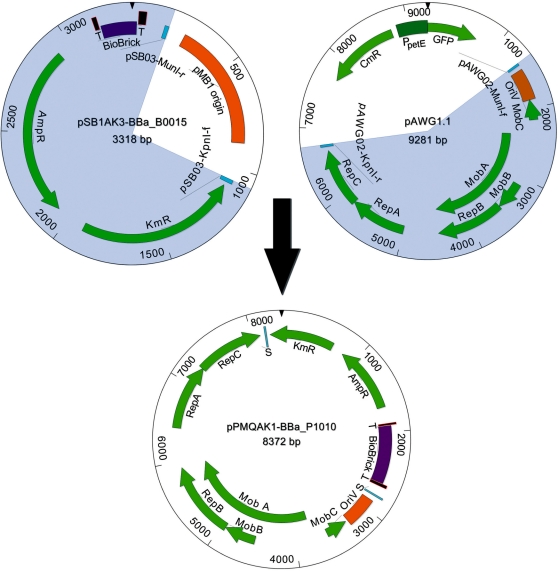
Figure 1.
Construction of the broad-host-range BioBrick shuttle vector pPMQAK1. The shaded 3318-bp DNA fragment of pSB1AK3-BBa_B0015, which includes the BioBrick cloning site containing part BBa_B0015 flanked by terminators and cassettes conferring resistance against ampicillin and kanamycin, was amplified with PCR using primers pSB03-KpnI-f and pSB03-MunI-r (Table 1). The shaded 9281-bp DNA fragment of pAWG1.1, which includes the replicon derived from RSF1010, was amplified with PCR using primers pAWG02-MunI-f and pAWG02-KpnI-r (Table 1). Intermediate plasmid pPMQAK1-BBa_B0015 (data not shown) was formed by digesting the two DNA fragments with KpnI and MunI and joining the resulting fragments. Finally, BioBrick part BBa_B0015 was exchanged with part BBa_P1010 to produce the pPMQAK1-BBa_P1010 plasmid. Abbreviations: BioBrick (BioBrick cloning site), T (double transcriptional terminator BBa_B0015), AmpR (ampicillin resistance cassette), KmR (kanamycin resistance cassette), CmR (chloramphenicol resistance cassette), RepA, RepB and RepC (replication proteins A, B and C), MobA, MobB and MobC (mobilization proteins A, B and C), OriV (vegetative origin of replication), GFP (green fluorescent protein), PpetE (petE promoter) and S (ligation site of the two DNA fragments).