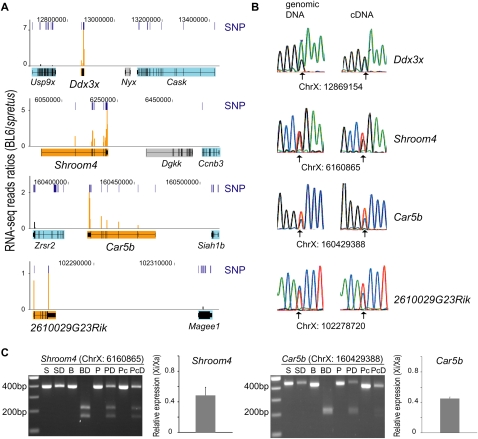
Figure 1.
RNA-seq identification of four novel escape genes (Ddx3x, Shroom4, Car5b, 2610029G23Rik). The escape genes are shown with six adjacent genes subject to X inactivation (Usp9x, Cask, Ccnb3, Zrsr2, Siah1b, Magee1). (A) RNA-seq data are graphed as the sequence read ratio (orange bars) between BL6 (inactive X) and M. spretus (active X) at each SNP (short, dark-blue bars) identified in the four escape genes (filled in orange). A few SNPs had ratios higher than those at the maximum scale (Supplemental Table S1). Flanking genes subject to X inactivation (filled in light blue) have very low BL6/spretus ratios. The inactivation status of the genes filled in gray is unknown due to the absence of expressed SNPs. Data were uploaded into the UCSC Genome Browser (Mouse July 2007 [mm9] assembly). (Top) Chromosome X coordinates. (B) Validation of SNPs and of bi-allelic expression of the escape genes by conventional sequencing of PCR and RT-PCR products. Chromatograms are shown for genomic DNA and cDNA with SNP coordinate underneath. (Arrows) Heterozygous bases. (C) Quantification of escape level of Shroom4 and Car5b. Genomic DNA and cDNA were amplified by PCR, followed by restriction endonuclease digestion. Products were separated by gel electrophoresis as shown in the gel pictures (SNP coordinate on top). (S) M. spretus DNA; (SD) M. spretus DNA digested; (B) BL6 DNA; (BD) BL6 DNA digested; (P) Patski genomic DNA; (PD) Patski genomic DNA digested; (Pc) Patski cDNA; (PcD) Patski cDNA digested. Graphs at right of the gels show relative expression levels from the inactive X (Xi) versus the active X (Xa) after real-time qPCR analyses.