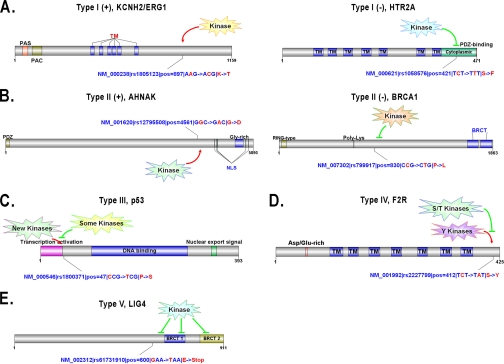
Fig. 2.
Five types of phosSNPs with typical examples. A, Type I PhosSNP. The K897T nsSNP of KCNH2/ERG1 creates a new AKT-specific phosphorylation site (Type I (+)), whereas the S421F nsSNP of HTR2A removes the phosphorylation site at Ser-421 (Type I (−)). B, Type II PhosSNP. The G4561D nsSNP of AHNAK might render its nearby Thr-4564 residue as a potential phosphorylation site (Type II (+)), whereas the P830L nsSNP of BRCA1 might prohibit Ser-832 phosphorylation (Type II (−)). C, Type III PhosSNP. The P47S nsSNP of p53 might induce changes of PK types for multiple adjacent phosphorylation sites. D, Type IV PhosSNP. The S412Y nsSNP of F2R might induce a change of its upstream serine/threonine PKs into tyrosine PKs. E, Type V PhosSNP. The E600Stop nonsense nsSNP might remove its following phosphorylation sites. TM, transmembrane.