Figure 2. Radio frequency PELF pulse sequences for 2D SLF spectroscopy of solids.
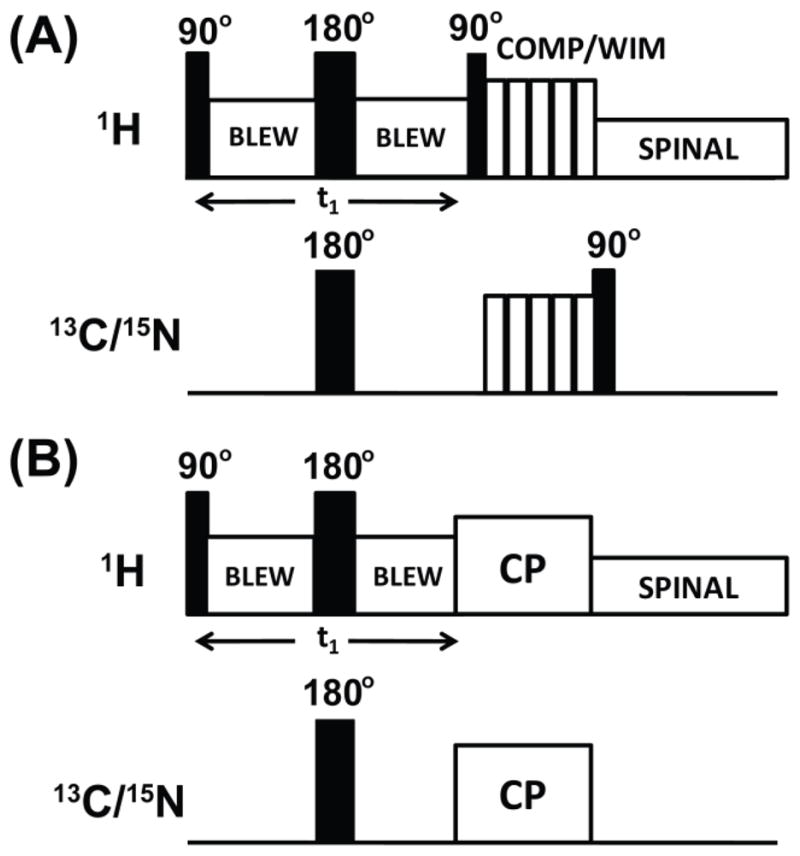
In these pulse sequences, proton homonuclear decoupling in the t1 period is achieved using the BLEW-12 sequence and SPINAL-64 is used to decouple protons during acquisition. Proton transverse magnetization after the t 1 period is transferred to X nuclei using the COMPOZER-CP or WIM pulse sequence. (A) or by the standard cross-polarization sequence (B). A supercycled COMPOZER sequence consists of a series of 360° pulses with phases x, −x, y, −y, −y, y, −x, x. The WIM sequence consists of a series of 90° pulses of phases −x, y, −x, −x, y, −x, x, y, x, x, y, x. Since the z-component of proton magnetization is transferred as the z-component of 15N or 13C spin magnetization under both WIM and COMPOZER-CP sequences, a 90° read pulse on the 15N or 13C channel is used for detection.
