FIGURE 4. Superpositioning of structural models of the guanosine binding site from different group I introns crystal structures reveal subtle differences.
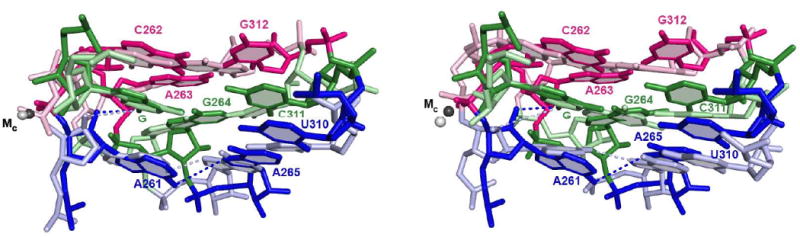
Model from the Azoarcus intron, PDB IS 3bo3 (41), is depicted in darker colors; models from the Tetrahymena intron (34) are in lighter colors and correspond to molecule C from the Tetrahymena ribozyme crystals (part A) and molecule A (part B). Numbering of residues is according to the Tetrahymena intron. Structures were superimposed by aligning the guanosine nucleophile (G). Nucleobases proposed to be part of the same base triple are depicted in the same color. Dashed lines connect the 2′-hydroxyl group of residue A261 and the exocyclic nitrogen atom of G, representing the hydrogen bond functionally detected and investigated herein, and the exocyclic nitrogen atom of residue A261 and the N7 atom of residue A265, representing a hydrogen bond proposed to stabilize the guanosine-binding site. Numerous other proposed hydrogen bonds within this site are omitted for clarity.
