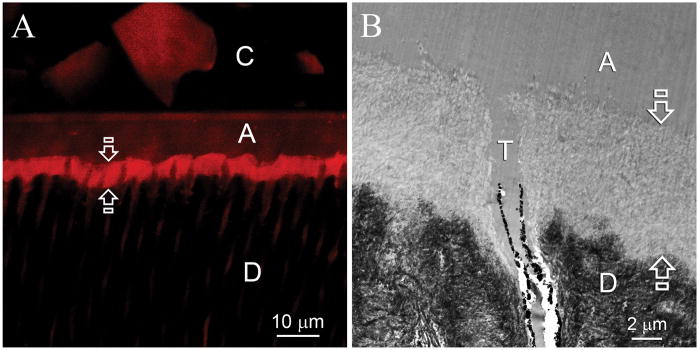
Fig. 2.
Representative confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images obtained from six months old specimens that had not been subjected to biomimetic remineralization. C: composite; A: adhesive; D: intertubular dentin. A. CLSM image showing that the entire hybrid layer (between open arrows) was permeable to Rhodamine B (Mw 479). B. TEM of the resin-dentin interface showed that the smear layer was completely dissolved. Etching of the underlying intact intertubular dentin by the aggressive one-step self-etch adhesive resulted in the formation of a 5–8 μm thick layer of completely demineralized collagen matrix (between open arrows) that was simultaneously infiltrated by the adhesive resin. Smear plugs were absent from the orifices of the dentinal tubules (T).