Fig. 2.
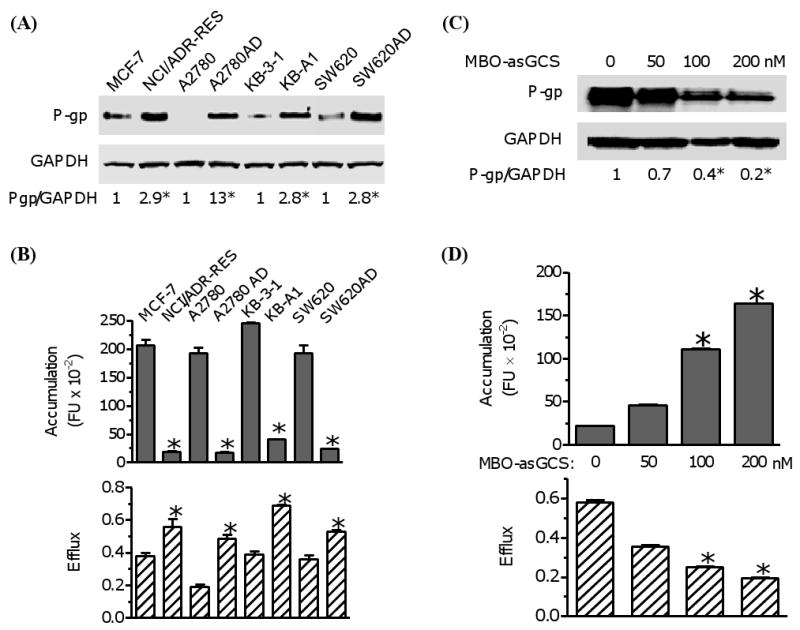
Examination of cellular accumulation and efflux in diverse cancer cell lines. (A) P-gp protein levels. Equal amount of detergent-soluble cell proteins (50 μg/lane) were resolved using SDS-PAGE and were immunoblotted with anti-P-gp antibody. The levels of P-gp were presented in the ratios of P-gp/GAPDH densities. *, p<0.001 compared with drug-sensitive counterpart. (B) Cellular accumulation and efflux of cancer cells. Cells were incubated with Flutax-2 (0.5 μM) for 2 hr to measure the accumulation. After washing, the cells were incubated in fresh medium for additional 2 hr to measure the efflux. *, p<0.001 compared with drug-sensitive counterpart. (C) P-gp in cells after MBO-asGCS treatment. NCI/ADR-RES cells were treated with MBO-asGCS for 6 days. Equal amount of detergent-soluble proteins (50 μg/lane) were resolved and were immunoblotted with anti-P-gp antibody. *, p<0.001 compared with vehicle control. (D) The accumulation and efflux of cells after MBO-asGCS treatment. After MBO-asGCS treatments, NCI/ADR-RES cells were incubated with Flutax-2 (0.50 μM) for accumulation and efflux assay. *, p<0.001 compared with vehicle control.
