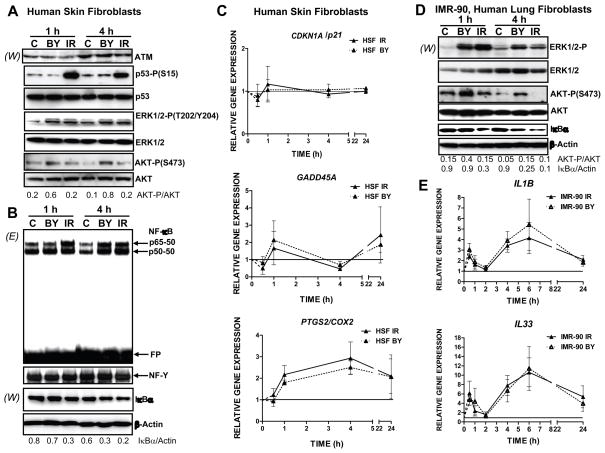
Fig. 1.
The main signaling pathways induced in directly irradiated and bystander fibroblasts. (A, B) Expression levels of indicated proteins from the control, bystander and α-irradiated human skin fibroblasts (HSF) were determined 1 and 4 h after treatment by Western blot analysis (W). EMSA (E) was performed for determination of DNA-binding activity of nuclear NF-κB and NF-Y transcription factors. Two main NF-κB DNA-binding complexes are indicated. Ubiquitous NF-Y activity was used as an internal control of the nuclear protein loading. Position of the free labeled probe (FP) is indicated. (C) Time course of gene expression of CDKN1A/p21, GADD45A and PTGS2/COX2 in directly irradiated (IR) and bystander cells (BY) at 0.5, 1, 4, and 24 h after irradiation, was determined by quantitative real time PCR and normalized to Ubiquitin C (UBC). Values are relative to time matched controls (solid line at 1). Points are the mean and standard error of three independent experiments. (D) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins from the control, bystander and α-irradiated IMR-90, human lung fibroblasts. (E) Time course of gene expression of IL1B and IL33 in directly irradiated and bystander IMR-90 fibroblasts.