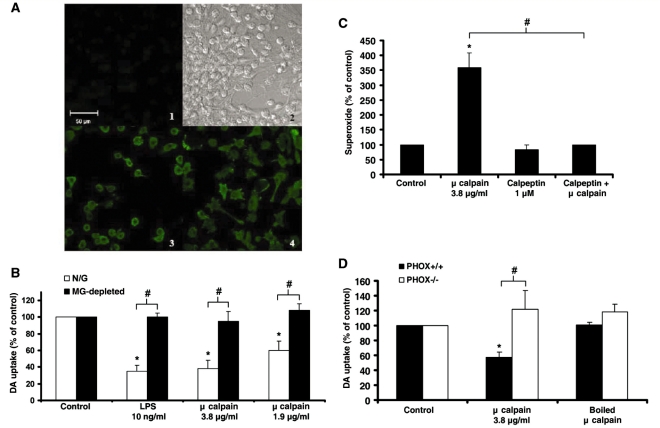
Figure 5.
Extracellular μ-calpain is neurotoxic due to activation of microglial NADPH oxidase. (A) Confocal images of neuron-glia cultures stained for ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule-1. Cells were treated with either vehicle (medium alone) or μ-calpain (3.8 μg/ml) for 12 h at 37°C. (1) Background fluorescence (no secondary antibody added); (2), transmitted light (Differential Interference Contrast) image; (3) untreated control cells; (4) μ-calpain-treated cells. The fluorescence micrographs depict representative changes in morphology caused by μ-calpain that indicates microglial activation. Activated microglial cells are amoeboid with multiple extended processes (4). The scale bar indicates 50 μm. (B) Neuron-glia cultures (N/G—containing microglia, astrocytes, and neurons) and microglia-depleted cultures (MG-depleted—containing astrocytes and neurons) were treated with medium alone (Control), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) 10 ng/ml (positive control for microglia-mediated neurotoxicity) or μ-calpain (3.8 or 1.9 μg/ml). Dopamine neurotoxicity was measured 9 days later with the [3H] dopamine uptake assay. μ-Calpain was only toxic in the presence of microglia. (C) Enriched microglia cultures were treated with medium alone (Control), μ-calpain (3.8 μg/ml), calpeptin (1 μM, a specific calpain inhibitor) or calpeptin + μ-calpain. The production of extracellular superoxide was measured by the superoxide dismutase-inhibitable reduction of tetrazolium salt, WST-1 at 30 min post-treatment. Results are mean ± SEM. Data are from four separate experiments. *P < 0.05, compared with control cultures. (D) Mesencephalic midbrain neuron-glia cultures from PHOX+/+ and PHOX−/− mice were treated with medium alone (Control), μ-calpain (3.8 μg/ml) or boiled μ-calpain (3.8 μg/ml). Graphs show the results expressed as percentage of the control cultures and are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in triplicate. *P < 0.05, control compared to treatment; #P < 0.05 indicates significant differences due to microglia (N/G versus microglia), superoxide reduction (calpeptin reduction of μ-calpain) or mouse strain (PHOX+/+ versus PHOX−/−).