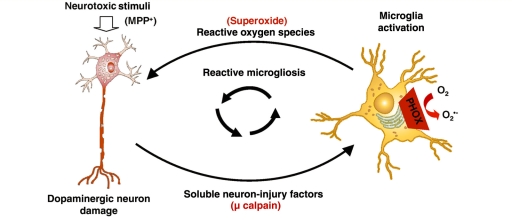
Figure 7.
μ-Calpain is a key factor driving the progressive nature of dopaminergic neuron damage. Dopaminergic (DA) neuron damage is chronic in part because damaged cells release soluble factors that accumulate over time to active resident microglia, driving further toxicity (reactive microgliosis). μ-Calpain is externalized in the process of dopamine neuron damage and is a fundamental soluble neuron injury factor responsible for the toxic aspects of reactive microgliosis. Specifically, extracellular μ-calpain activates microglial NADPH oxidase, producing superoxide to damage neighbouring dopaminergic neurons selectively and propagate neurotoxicity. This feed-forward cycle provides much needed insight into the progressive nature of dopaminergic neuron damage.