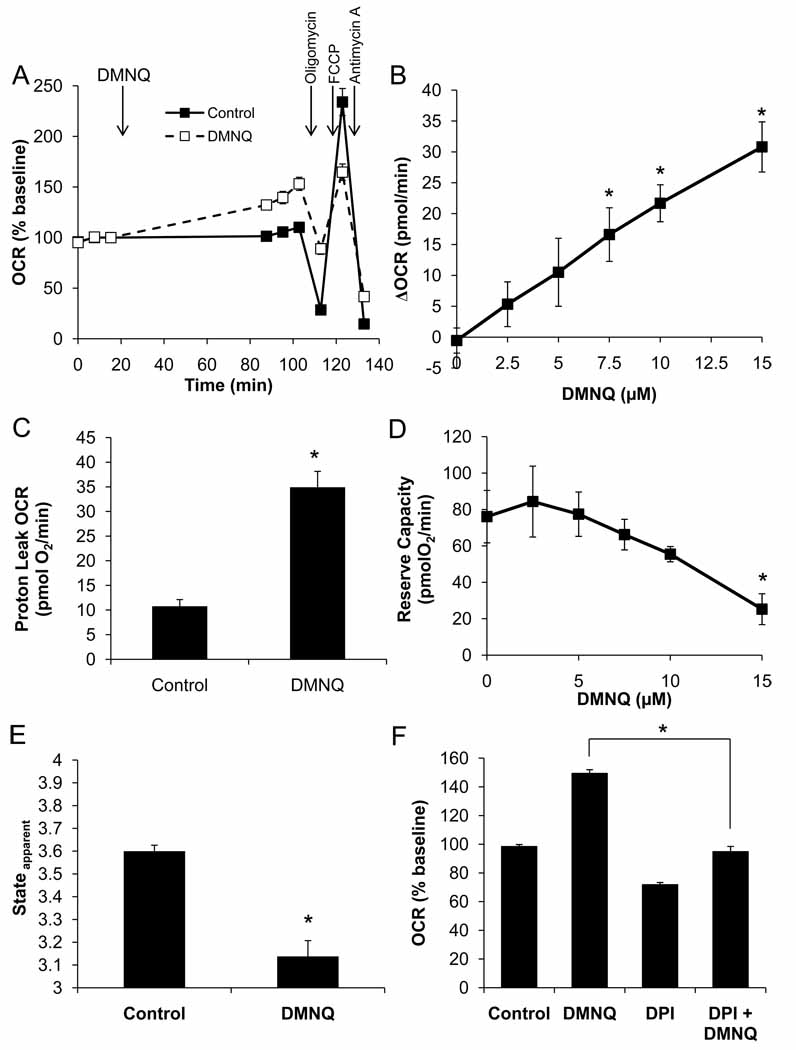
Figure 6. Acute DMNQ treatment decreases maximal OCR.
BAEC were seeded at 40,000 cells/well and allowed to grow for 24 h. Three baseline measurements of OCR and ECAR were made, and then cells were treated with DMNQ (15 µM) for 1 h. Following this treatment, three further measurements were performed prior to sequential injection of oligomycin (1 µg/ml), FCCP (1 µM), and antimycin A (10 µM) to determine mitochondrial function (Panel A). Panel B: The increase in basal OCR due to DMNQ was determined and is plotted as a function of DMNQ concentration. Panel C: Proton leak was calculated and is shown for control and DMNQ (15 µM)-treated cells. Panel D: Reserve capacity following DMNQ treatment is also plotted as a function of DMNQ concentration. Panel E: Apparent respiratory state was calculated as described and is shown for control and DMNQ (15 µM)-treated cells. Panel F: Diphenyleneiodonium (10 µM) was added with the DMNQ in some treatment groups. Inhibition of DMNQ-dependent OCR stimulation is shown. Data shown are the mean ± sem, n≥3 per group. *, p<0.05 vs. Control unless indicated otherwise.