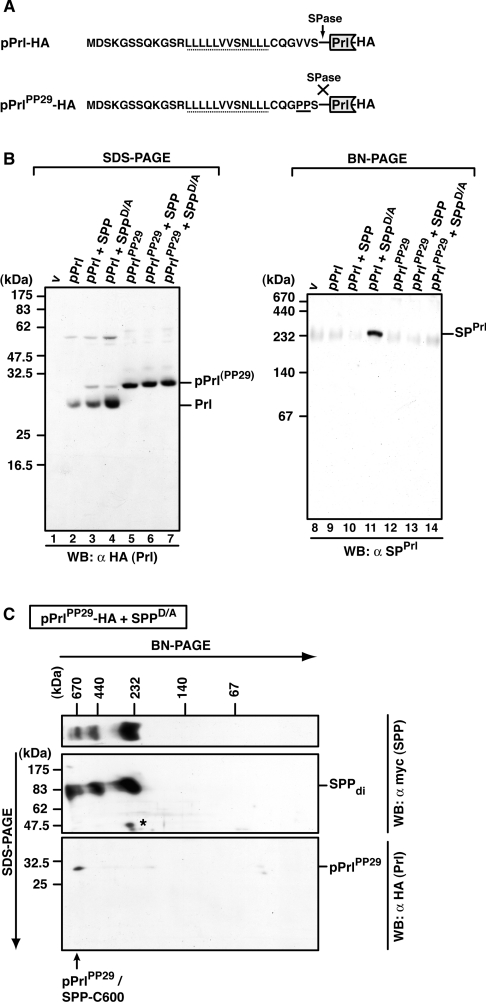
Figure 7. Identification of pPrl–SPP complexes.
(A) Amino acid sequence of the signal sequence of wild-type pPrl and the mutant pPrlPP29, which is not cleaved by signal peptidase (SPase) (both are C-terminally HA-tagged). The V→P mutation (PP29) is underlined. h-regions are indicated with a dotted line. (B) Detection of mature prolactin (Prl), pPrlPP29 and SPPrl after SDS/PAGE or BN-PAGE. HEK-293 cells transiently expressing pPrl–HA or pPrlPP29–HA alone or together with SPP–myc or SPPD/A–myc were lysed with 1% digitonin, and total lysates were subjected to Tris/glycine SDS/PAGE (lanes 1–7) or to BN-PAGE (6–16%; lanes 8–14). Mature prolactin (Prl–HA) and pPrl(PP29)–HA were identified after SDS/PAGE by Western blotting (WB) using anti-HA antibodies, and SPPrl was identified after BN-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-SPPrl antibodies. v, empty vector control. (C) Identification of pPrlPP29 in the 600 kDa SPP complex after 2D-BN-SDS/PAGE. HEK-293 cells transiently co-expressing pPrlPP29–HA and SPPD/A–myc were lysed with 1% digitonin, and the total lysate was first separated by BN-PAGE (6–13%) and then in the second dimension by SDS/PAGE (12.5%). SPPD/A–myc complexes and pPrlPP29–HA were identified by Western blotting (WB) using the anti-myc and the anti-HA antibody respectively. SPP dimers (di) and pPrlPP29/SPP-C600 are indicated. The asterisk indicates a cross-reacting band. Molecular masses are indicated in kDa.