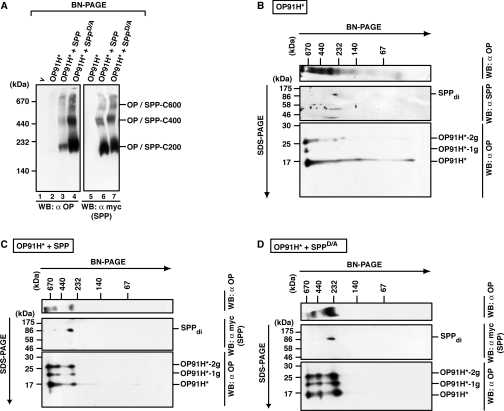
Figure 8. Misfolded opsin accumulates in several SPP complexes.
(A) Identification of OP91H*–SPP complexes after BN-PAGE. HEK-293 cells transiently expressing OP91H* and SPP–myc or SPPD/A–myc as indicated were lysed with 1% digitonin, and aliquots were separated by BN-PAGE (5–9%). OP91H* and SPP/SPPD/A–myc complexes were identified by Western blotting (WB) using anti-opsin and anti-myc antibodies respectively. SPP complexes of 200 kDa (SPP-C200), 400 kDa (SPP-C400) and 600 kDa (SPP-C600) co-migrating with OP91H* are indicated. (B–D) Glycosylated and non-glycosylated opsin is found in complexes of the same size. Digitonin lysates of HEK-293 cells transiently expressing OP91H* (B) or co-expressing SPP–myc (C) or SPPD/A–myc (D) were first separated by BN-PAGE (6–13%) and then separated in the second dimension by SDS/PAGE (15%). Top panels show Western blots (WB) of the BN gels using anti-opsin antibodies. Middle panels show Western blots of the upper part of the second-dimension SDS gels using anti-SPP antibodies in (B) and anti-myc antibodies in (C) and (D). Bottom panels show Western blots of the lower part of the second-dimension gel using anti-opsin antibodies. SPP dimers (di) and non-, mono- (−1g) and bi- (−2g) glycosylated forms of OP91H* are indicated. Molecular masses are indicated in kDa.