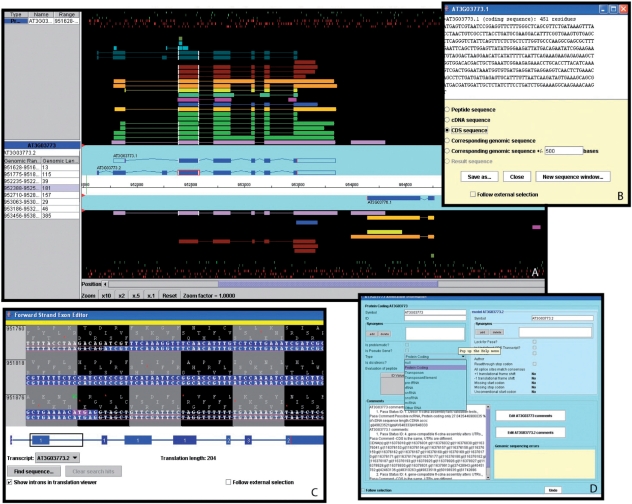
Figure 6.
A selection of windows from the Apollo genome annotation tool. (A) The main Apollo window contains two sections: the section with the turquoise background displays all current gene models in the selected region; the section with the black background shows different types of sequences aligning to either strand of the genome. Sequences include Arabidopsis ESTs (light purple) and cDNAs (green), gene models from alternative prediction tools (gold: Gnomon, yellow: Eugene, turquoise: Augustus), Brassica ESTs (blue), sequences from five different monocot species (deep purple), radish clones (brown), and short peptides (light blue, dark green). The side panel provides additional information about the selected sequence and the genomic coordinates and length of each of its exons. By right-clicking on a gene model, a menu pops up which opens a series of useful additional windows, including: (B) the ‘Sequence’ window displaying the sequence of the selected model. From a list of radio buttons, the type of a displayed sequence can be selected (peptide, cDNA, CDS, genomic sequence). (C) The ‘Exon Detail Editor’ showing the genome sequence corresponding to the selected gene as well as the protein sequence in all three frames. Annotated exons are displayed as blue boxes that can be pulled back and forth to modify the boundaries of each exon. (D) The ‘Annotation Info Editor’ allows the user to edit the name of a gene, modify the gene type and add comments about a gene model and its annotation.