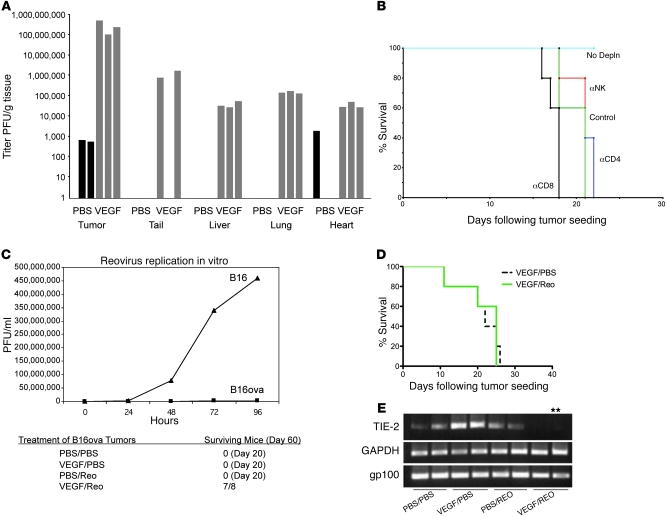
Figure 2. VEGF165 sensitization to Reo therapy involves host cells.
(A) Viral titers from organs of mice bearing 10-day tumors treated with a single injection per day for 3 consecutive days of VEGF165 or PBS, followed 24 hours later by a single i.v. injection per day for 2 consecutive days of Reo. (B) Mice bearing 5-day established B16 tumors (5/group) were left intact (2 i.p. injection of IgG, days 6, 7 [No Depln]) or were depleted of CD8 (α-CD8), CD4 (α-CD4), or NK cells (α-NK). Mice were then treated (days 8–10) with VEGF165 or PBS, followed by Reo or PBS (control) (days 11, 12) as in A. (C) Top panel: viral titers recovered from B16ova or B16 cells infected in vitro with Reo (MOI 0.1). Bottom panel: mice bearing 7-day established B16ova tumors were treated with VEGF165 or PBS (days 1–3), followed by Reo or PBS (days 4, 5) as in A. This regimen was repeated (days 8–12 and 15–19) twice. Mice surviving by day 60 are shown. (D) MyD88-deficient mice bearing 7-day established B16 tumors (7–8/group) were treated with VEGF165 or PBS (days 1–3) followed by Reo or PBS (days 4, 5) as in A. This regimen was repeated (days 8–12 and 15–19) twice. (E) RT-PCR with primers for endothelial TIE2, tumor-specific gp100, or GAPDH using RNA from B16 tumors 48 hours following 2 i.v. injections of PBS or Reo 24 hours following 3 consecutive daily injections of either VEGF165 or PBS. **Positive for TIE2 upon nested PCR.