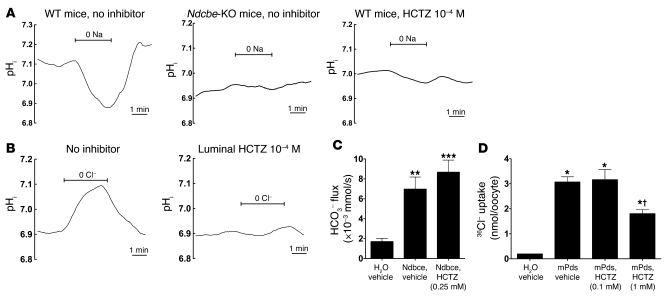
Figure 7. Effects of HCTZ (10–4 M) on NDCBE or PDS activity in isolated collecting ducts or on recombinant NDCBE or PDS expressed in Xenopus oocytes.
(A) Effects of HCTZ and Ndcbe disruption on Na+-dependent pHi changes measured in intercalated cells of CCD isolated from Na-depleted Ndcbe–/– or Ndcbe+/+ mice fed a low-Na+ diet. Traces are the average of pHi changes recorded when luminal Na+ was removed and then readded, in the presence of extracellular Cl– (122 mM) and HCO3– (25 mM). Intracellular Na+-dependent acidification was detected in Ndcbe+/+ mice but absent in Ndcbe–/– mice or when HCTZ 10–4 M was present in the perfusate. In these 3 different experimental conditions, mean starting pHi values were 7.10 ± 0.02, 6.93 ± 0.11, and 7.01 ± 0.04, respectively. (B) Effects of HCTZ on apical Cl–/HCO3– exchange activity in intercalated cells of CCDs isolated from Na-depleted animals. Traces are the average of pHi changes recorded when luminal Cl– was removed and then readded, in the presence of extracellular HCO3– (25 mM) and in Na+-free solutions. Intracellular Cl–-dependent alkalinization, reflecting apical Cl–/HCO3– exchange, was completely abolished when 10–4 M HCTZ was present in the perfusate. Mean starting pHi values (immediately before Cl– removal) were 6.91 ± 0.03 and 6.89 ± 0.08, in the absence and presence of HCTZ, respectively. (C) Effects of HCTZ on mNdcbe-mediated HCO3– influx. Oocytes had been injected with mNdcbe cRNA or H2O and incubated with HCTZ (0.25 mM). As a control, NDCBE-expressing and H2O-injected oocytes were incubated with vehicle (methanol). Values are mean ± SEM with 6–9 oocytes per group. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus H2O-injected oocyte. HCO3– flux was unaffected by the application of HCTZ (0.25 mM) compared with vehicle alone (P = 0.279). (D) Effects of HCTZ on Pds-mediated 36Cl– uptake. Pendrin-expressing oocytes (mPds) were incubated in ND96 containing 0.1 or 1 mM HCTZ during the uptake period (16 minutes). As a control, pendrin-expressing and H2O-injected oocytes were incubated with vehicle (methanol). Values are mean ± SEM, with 6–16 oocytes per group. *P < 0.001 versus H2O; †P < 0.001 versus mPds, HCTZ 0.1 mM.