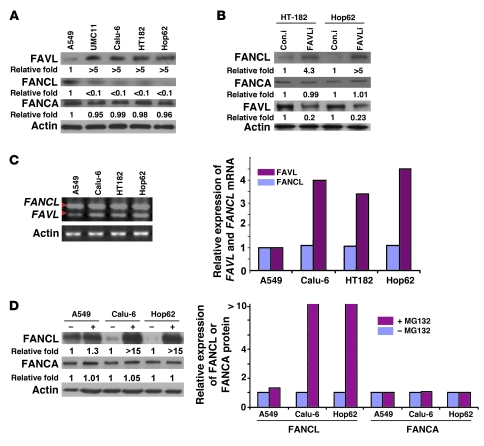
Figure 4. FAVL impairment of the FA-BRCA pathway is attributed to a low level of FANCL, resulting from FAVL regulation at posttranslational level.
(A) The level of FANCL protein, not that of FANCM (data not shown) or FANCA, is low in cells expressing high levels of FAVL compared with A459 cells. (B) Downregulating FAVL enhances levels of FANCL protein but not those of FANCM (data not shown) or FANCA. (C) Levels of FANCL mRNA remain similar among cells expressing low and high levels of FAVL. The ethidium bromide intensity of the high band (indicating the expression level of FANCL mRNA) in each reaction appears to be similar, but the intensity for the low band (indicating the expression level of FAVL mRNA) is stronger in HT182, Hop62, and Calu-6 cells than in A549 cells. (D) FANCL protein can be clearly detected in Calu-6, HT182, and Hop62 cells after MG132 treatment. Total cell lysates were prepared from Calu-6, HT182, and Hop62 cells, treated with or without 10 μM MG132 for 20 hours. Levels of FANCL, FANCM, and FANCA protein were analyzed. FANCL protein level was increased clearly in cells treated with MG132 compared with control cells but not too much for FANCM protein (data not shown) or FANCA protein. Relative expression levels of FA proteins tested were generated using the level of gray intensity of Western bands, measured using the NIH ImageJ program. (A, B, and D) Relative fold level increase is shown for each protein.