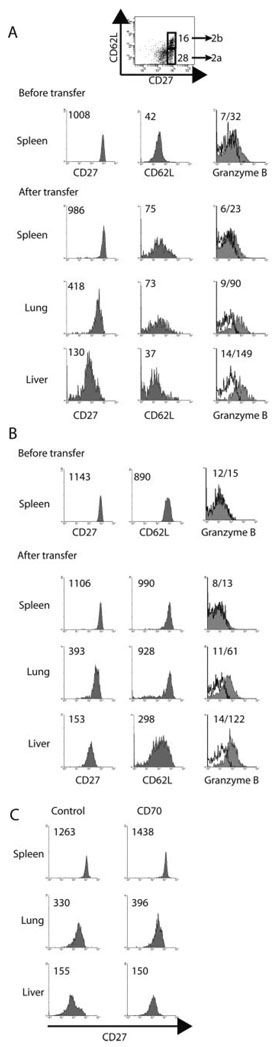
FIGURE 2.
Splenic CD8 TCM down-regulate CD27 and acquire granzyme B after entry into nonlymphoid tissues. OT-I transferred CD45.2 mice were infected with 1 × 103 CFU of LM-ova i.v. 48 days later mice were re-infected with 1 × 106 PFU VSV-ova i.v., and 97 days later, splenocytes were isolated, enriched for CD8 T cells, donor cells were sorted into either CD62Llow/CD27high cells (A) or CD62Lhigh/CD27high cells (B) and transferred to naive CD45.2 mice (1×106 and 5×105, respectively). Four days later lymphocytes were isolated from the spleen, lung, and liver, and the level of CD27, CD62L, and granzyme B expression by the transferred OT-I T cells was determined. C, OT-I transferred mice were infected with LM-ova i.v.; 46 days later mice were infected with VSV-ova i.v., and 58 days later splenocytes were isolated, enriched for CD8 T cells, donor cells were sorted, and 8.5 × 105 CD27high cells were transferred to naive CD45.2 mice. On days 0, 1, and 2, mice were treated with either 250 µg of anti-CD70 (FR70) or control rat IgG. Four days later, lymphocytes were isolated from the spleen, lung and liver, and the level of CD27 was determined on the transferred OT-I T cells. Values indicate the MFI of staining for the population. For GrB staining the MFI is shown for the isotype control and test, respectively. Data are from one representative animal of 1–4 mice analyzed from four experiments (n = 9).