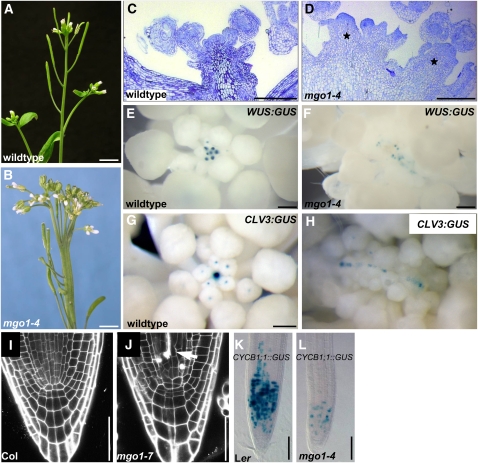
Figure 2.
mgo1 Meristem Phenotypes.
(A) and (B) Inflorescences of wild-type (A) and mgo1-4 plants (B). The mutant displays fasciation and fragmentation of the apex. Phyllotaxis and internode spacing is variable in mgo1-4 (B) in contrast with the stereotypic arrangement in the wild type (A).
(C) and (D) Inflorescence shoot meristems of wild-type (C) and mgo1-4 plants (D). The mgo1-4 inflorescence meristem displays multiple independent meristems (asterisks), each of which is generating floral primordia at its flanks.
(E) to (H) WUS:GUS and CLV3:GUS expression. In mgo1-4 mutants ([F] and [H]), expression of both stem cell niche markers is fragmentized into multiple domains arranged in a line, in contrast with the wild type ([E] and [G]).
(I) and (J) Confocal image of root meristems of 5-d-old seedlings of Columbia (Col) wild type (I) and mgo1-7 (J) plants. Dead cells, which accumulate propidium iodide, are marked by an arrow.
(K) and (L) The number of cells expressing the CYCB1;1:GUS reporter is strongly reduced in 5-d-old primary roots of mgo1-4 (L) versus Ler (K).
Bars = 5 mm in (A) and (B), 200 μm in (C) and (D), 50 μm in (E) to (H), 200 μm in (I) and (J), and 100 μm in (K) and (L).