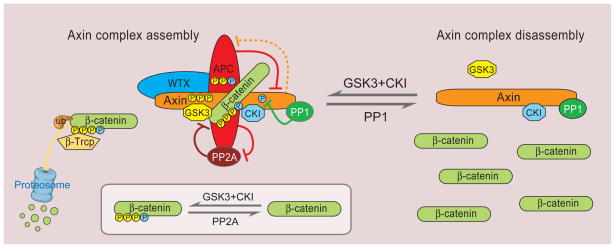
Figure 4. Regulation of Axin complex assembly for β-catenin degradation.
The core components of the Axin complex, Axin, APC, GSK3 and CK1 collectively promote β-catenin phosphorylation for degradation by β-Trcp. In addition to phosphorylating β-catenin, GSK3 (yellow) and CK1 (blue) also phosphorylate Axin and APC and enhance their binding to β-catenin and degradation complex stability, further ensuring β-catenin phosphorylation. The inset illustrates β-catenin phosphorylation (by CK1 and GSK3) and dephosphorylation (by PP2A). APC may also act to prevent PP2A dephosphorylation of β-catenin. APC paradoxically facilitates Axin degradation and possibly vise vesa (indicated by dashed line, see text). PP1 dephosphorylates Axin to antagonize CK1 phosphorylation and negatively regulates GSK3-Axin binding resulting in complex disassembly.