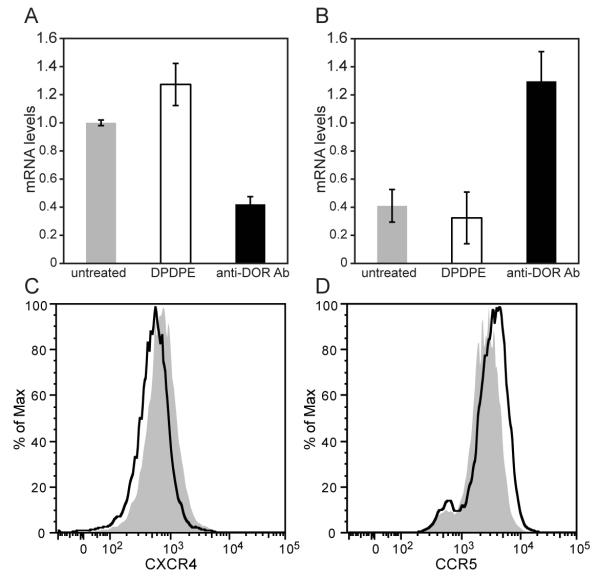
FIGURE 4.
Immunomodulation of chemokine receptor expression by anti-DOR autoantibodies. A, B, Real-time PCR analysis. CEM×174 cells (1×106) were incubated for 24 hours with 10 μM DPDPE or 100 μg anti-DOR autoantibodies. Total RNA was extracted from the cells and real-time PCR was performed using human specific primers for CXCR4, CCR5 and TATA box binding protein. Values were normalized against TATA box binding protein. There was a significant reduction in CXCR4 gene expression by anti-DOR antibody treated cells as compared to untreated cells (A, p<0.05). In contrast, anti-DOR antibody treatment significantly upregulated CCR5 expression (B, p<0.01). Paired t-test was performed to determine p values. Data is representative of three independent experiments. C, D, Flow cytometry analysis. CEM×174 cells were plated at 1×105 cells/well. The cells were treated with 10 μM DPDPE or 100 μg anti-DOR autoantibody. After 48 hours, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for surface expression of chemokine receptors. Treated and untreated cells are shown in black and grey histograms, respectively. Treatment with anti-DOR Ab reduced surface CXCR4 expression (C), while increasing CCR5 expression (D). There was no change in the expression of chemokine receptors after DPDPE treatment (data not shown).