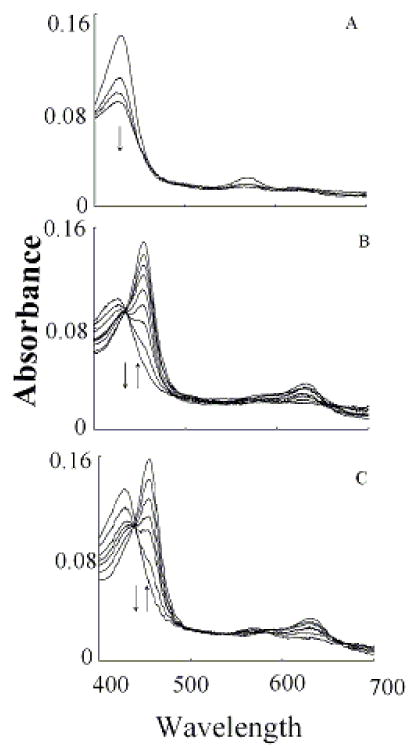
Fig. 3.
Trp accelerates the conversion rates of MPO Compound I to Compound II. Absorbance spectra of MPO recorded by diode array stopped-flow in the absence (Panels A and B) and the presence of 400 μM Trp (Panel C). Experiments were performed under aerobic condition when a phosphate buffer solution (200 mM, pH 7.0) containing 2.4 μM MPO in the absence and presence of either 200 μM were rapidly mixed with a buffer solution supplemented with 40 μM H2O2 at 10 °C as described under the Experimental Conditions section. Panel A contains spectra collected at 0.00, 0.001, 0.004, 0.07 s after mixing showing the formation of MPO Compound I. Panel B contains spectra collected at 0.015, 0.025, 0.105, 0.205, 0.305, 0.495, 0.950, 02.95 and 4.00 s after initiating the reaction showing the conversion of MPO Compound I to Compound II. Panel C contains spectra collected at 0.01, 0.07, 0.016, 0.022, 0.031, 0.049 and 2.85 s after mixing showing the direct conversion of MPO-Fe(III) to Compound II without the accumulation of Compound I. Arrows indicate the direction of spectral change over time.