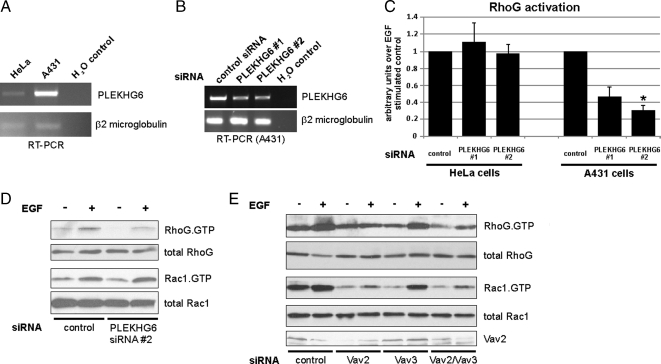
Figure 7.
PLEKHG6 and Vav-family GEFs are involved in EGF stimulated RhoG activation in A431 cells. (A) RT-PCR analysis with primers specific for PLEKHG6 was performed with total RNA samples from HeLa and A431 cells. RT-PCR of β2-microglobulin RNA served as a control. (B) To confirm knockdown with the PLEKHG6 siRNAs, RT-PCR analysis with primers specific for PLEKHG6 was performed with total RNA samples from A431 cells that have been transfected with control or one of two different PLEKHG6-specific siRNAs (PLEKHG6 #1, PLEKHG6 #2). RT-PCR of β2-microglobulin RNA served as a control. (C) A431 cells and HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or one of two different PLEKHG6-specific siRNAs (PLEKHG6 #1, PLEKHG6 #2). All cells were stimulated for 30 s with EGF before GST-ELMO pull-down assays were performed. The bar graphs represent RhoG activity 30 s after EGF treatment in PLEKHG6 knockdown conditions compared with siRNA controls (n = 3; error bars represent SEM). The asterisk indicates significant differences compared with control siRNA-transfected cells (p < 0.05). (D and E) A431 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs: control, PLEKHG6 #2 (D); control, Vav2, Vav3, and Vav2/Vav3 (E). Rapid activation of RhoG or Rac1 after 30 s EGF treatment was measured using GST-ELMO and GST-PBD pull-down assays, respectively.