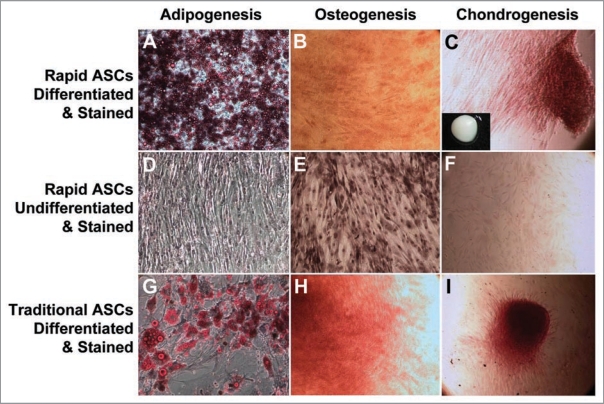
Figure 2.
Characterization of ASC differentiation. The differentiation potential of ASCs isolated in the streamlined, rapid protocol were compared to ASCs isolated using the standard protocol (traditional ASCs). Cells were induced to differentiate into adipocytes ((A) for rapid ASCs and (G) for traditional ASCs; (D) rapid ASCs grown for 2 weeks without adipogenic media as control; all stained with oil red O and hematoxlin), osteocytes ((B) for rapid ASCs and (H) for traditional ASCs; (E) rapid ASCs grown 2 weeks without osteocyte induction media as control; all stained with Alizarin red S and hematoxylin), and chondrocytes [(C) for rapid ASCs and (I) for traditional ASCs, both in a micromass (solid micromass pellet, insert, (C)]; (F) unpelleted rapid ASCs grown 4 weeks in induction media as control; all samples stained for Safranin O).