Figure 3.
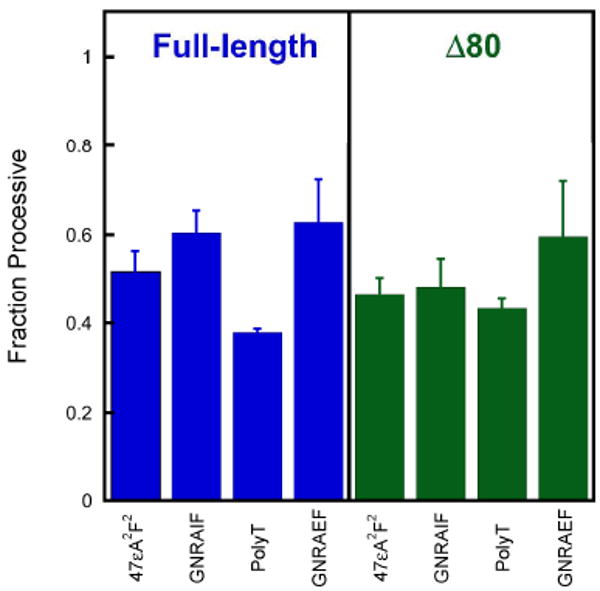
AAG searches both strands of DNA. To test whether hopping contributes to the searching mechanism of AAG, we measured the processivity for substrates in which lesions are on the opposing strands and compared this to a substrate in which the lesions are on the same strand (47εA2F2). See Figure 1 for the DNA sequences. Multiple-turnover processivity assays were performed at an ionic strength of 200 mM for full-length AAG (blue) or 115 mM for Δ80 AAG (green). Each column represents the average of at least two independent experiments with error bars indicating one standard deviation from the mean (n ≥ 4).
