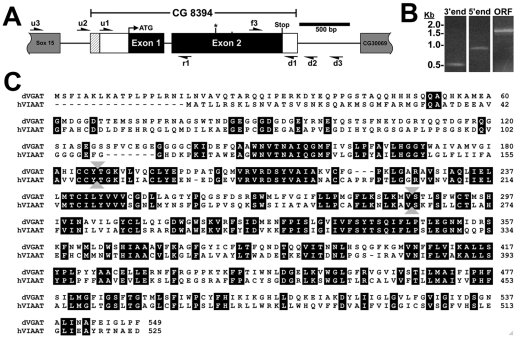
Fig. 1.
Cloning of the Drosophila vesicular γ-amino butyric acid (GABA) transporter (CG8394). (A) CG8394/dVGAT is between CG30069 and Sox15 on the right arm of chromosome II. Exons are shown as boxes, with coding sequence in black and untranslated sequence in white. Introns are indicated as black lines. The 5′ extent of the BDGP clone IP12576 is indicated with hatching. Arrows indicate primers used for RT-PCR to define the 5′ and 3′ extent of the cDNA and an asterisk indicates the insertion site of the minos element. (B) The approximate 3′ and 5′ extent of CG8394. Untranslated regions (UTRs) were mapped by selectively amplifying CG8394 products using primer pairs f3/d1 (3′ end) and r1/u1 (5′ end) but not more distal primers (see Results). RT-PCR to amplify the coding sequence shows a 1.7 kb product (ORF). Size markers are shown on the left, in kilobases. (C) The predicted amino acid sequence of dVGAT is shown aligned with human VIAAT/VGAT. Identities are highlighted. Identity at the amino acid level is 44%; for comparison dVGLUT shows 41% identity with human VGLUT orthologs (Daniels et al., 2004). Gray arrowheads between amino acids 118 and 119, and between 286 and 287 indicate the site of the mRNA splice junction and the insertion site of the minos element, respectively.