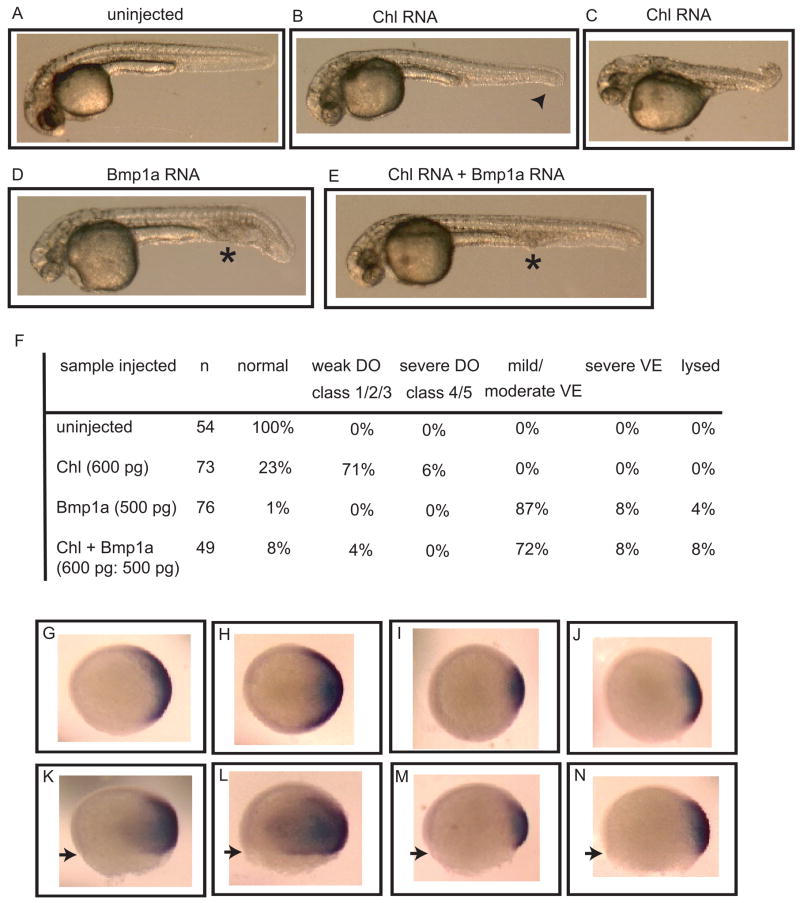
Fig. 5.
Effects on dorsoventral patterning by overexpression of Chl in the presence or absence of Bmp1a. Phenotypes are shown of an uninjected 24 hpf control embryo (A), 24 hpf embryos with mild dorsalizaiton (B) or moderate dorsalization (C) after injection with 600 pg Chl RNA, and 24 hpf embryos injected with 500 pg Bmp1a RNA (D), or a combination of 600 pg Chl and 500 pg Bmp1a RNA (E). An arrowhead marks partial tail fin loss, asterisks mark blood pooling; signs of mild dorsalization or ventralization, respectively. (F) Quantification of phenotypes at 24 hpf. Severity of dorsalization (DO) is numerically classified as per Mullins et al. (Mullins et al., 1996). Degree of ventralization (VE) was not numerically classified. Whole-mount in situ hybridization is shown (animal view, panels G–J; lateral view, panels K–N) for expression of the dorsal marker Chd at 70% epiboly for uninjected embryos (G and K) or embryos injected, as above, with RNA for Chl alone (H and L), Bmp1a alone (I and M), or both Chl and Bmp1a (J and N). Arrowheads mark extent of epiboly. All embryos in panels G–N are from the same clutch of eggs and same developmental stage.