Figure 1.
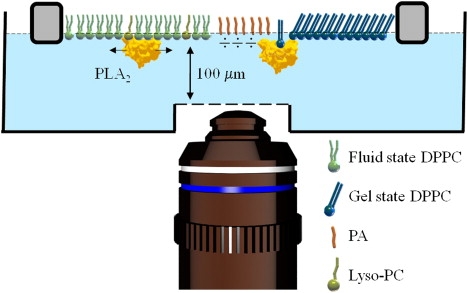
Schematic of the monolayer setup. A DPPC monolayer is compressed into the center of the phase transition region (Π = 8 mN/m, MMA = 65 Å2). At this surface pressure, liquid state lipid molecules (green) coexist with gel state lipid molecules (blue), which form domains. In this coexistence region, L-DPPC monolayers are susceptible to hydrolysis by PLA2-IB (yellow). Hydrolysis leads to formation and accumulation of ionized free palmitic acid (PA, red) and lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC, olive green) in the monolayer. The monolayer trough was custom-designed to accommodate the 200-μm working distance of the high numerical aperture objective (NA = 1.2) and mounted on a home-built epi-fluorescence microscope.
