Figure 1.
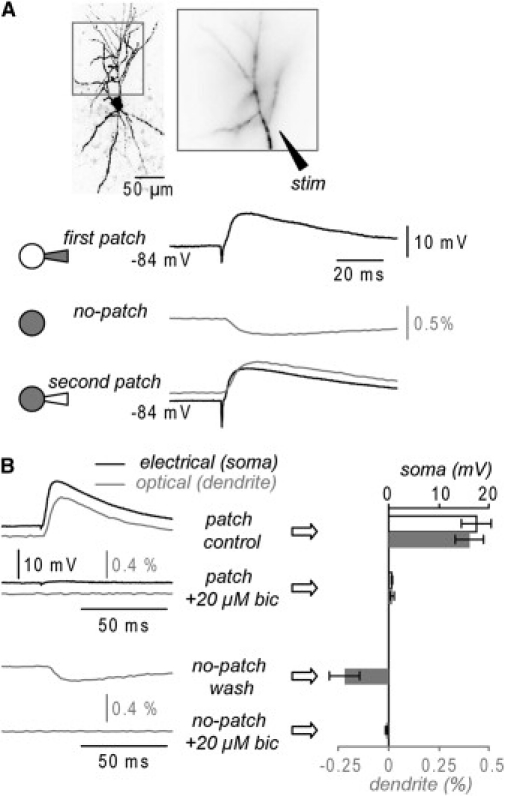
Optical measurements of GABA-mediated synaptic potentials (A) (Top) Fluorescence image of a CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neuron (left). Dendritic region in recording position (right). (Upper trace) Electrical somatic recording (black) of a depolarizing evoked synaptic potential during dye loading with 40 mM Cl− internal solution (first patch). (Middle trace) Hyperpolarizing synaptic potential evoked by the same stimulus and recorded optically as spatial average from all dendrites after electrode removal (no-patch). (Bottom trace) Superimposed electrical somatic (black) and optical dendritic (gray) recordings of the synaptic potential after repatch with an electrode containing 40 mM Cl− (second patch). Synaptic potentials are averages of nine trials. (B) (Left/top) Electrical (black) and optical (gray) dendritic synaptic potential recordings during loading (40 mM Cl−) before and after addition of 20 μM bicuculline. (Left/bottom) optical dendritic recordings 30 min after patch termination and bicuculline washout before (upper trace) and after (lower trace) reapplication of bicuculline. (Right/top) Synaptic potential peak amplitude (mean ± SD; n = 5 cells) for electrical (white) and optical (gray) signals during loading before and after addition of 20 μM bicuculline. (Right/bottom) Optical synaptic potential signal peak amplitude (mean ± SD; n = 5 cells) after electrode removal before and after addition of bicuculline. Effects statistically significant (p < 0.01, paired t-test).
