Fig. 1.
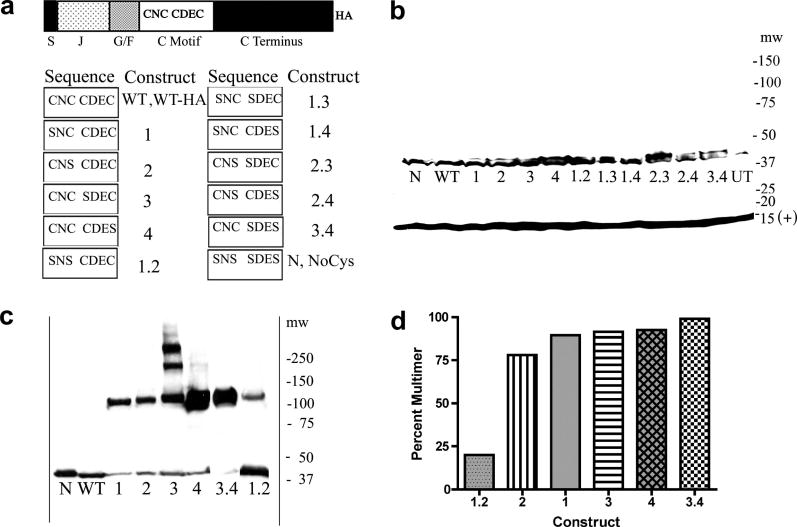
A. Domain structure of HEDJ, sequence of mutant constructs, nomenclature. Domains are labeled as follows: S, signal sequence; J, J domain; G/F, Gly/Phe rich; C motif, Cys-rich; C terminus, carboxyl-terminal domain; HA, hemagglutinin tag. The amino acids present in the Cys motifs of each mutant are listed in the columns marked Sequence and the corresponding names for each mutant are listed to the left, under the columns labeled Construct. B. WT-HA and mutant HA-tagged forms of HEDJ are expressed at similar levels. The proteins in TCA precipitated lysates from transfected COS-1 cells, were separated by using SDS-PAGE, 4–15%, with reducing conditions and immunoblotted with rabbit anti-HA antibody and rabbit anti-Sec 61β antibody (marked (+) at 14 kDa) which served as a loading control. Molecular weight markers (mw) are listed on the right. C. All the single Cys mutants and two double mutants, 3.4 and 1.2, form intermolecular disulfide-bridged multimers. Samples were processed as in B. except pellets were suspended in non-reducing SDS-PAGE sample buffer with 40 mM NEM and immunoblotting was done using mouse anti-HA antibody. The mobilities of WT and N are shown for comparison. D. Approximate quantification of the percent of the multimeric form present in each mutant in C.