Fig. 5.
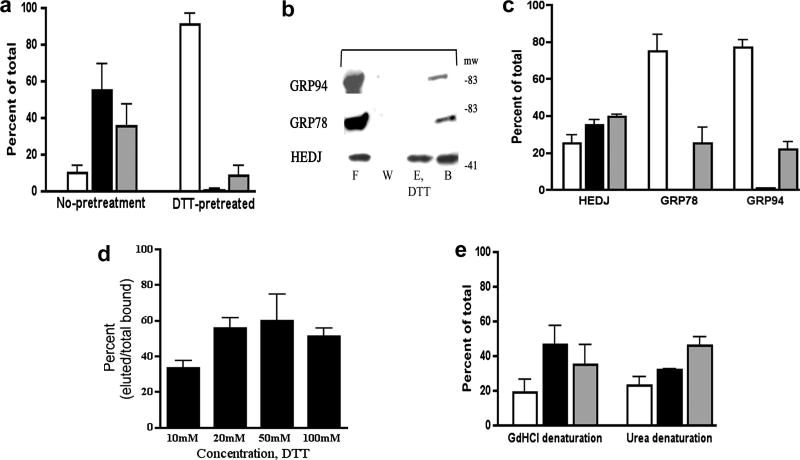
A. Pretreatment of HEDJ with reducing agent prevents initial binding to dTg. Lysed microsomes were pre-incubated in binding buffer with or without 50 mM DTT, prior to incubation with immobilized dTg. DTT pretreated refers to samples that were pretreated, washed and eluted with 50 mM DTT. No pretreatment indicates that 50 mM DTT was included only in the elution buffer. Open columns, F; black, E; gray, B. There was significantly more HEDJ in the flow-through and wash fraction (F) of samples pretreated with DTT as compared to the control. (p< 0.02, n=3, t test) B. HEDJ can be partially eluted from dTg with DTT while binding by GRP78 and GRP94 is not affected. Immobilized dTg, denatured with urea and 2-mercaptoethanol, was processed as in Figure 4A. The elution buffer contained 100 mM DTT. C. Quantification of chaperone binding and DTT elution experiments. The amount of HEDJ in the eluted fraction (E, DTT) was significantly higher in the case of HEDJ as compared with GRP78 or GRP94. (p<0.05, unpaired t test, n=2). D. The effect of DTT concentration on the fraction of HEDJ eluted from dTg. Experiments were done as in B. except 10, 20, 50, or 100 mM DTT was used for the elution step. The proportion of HEDJ eluted with 20, 50 or 100 mM DTT was significantly higher than that eluted with 10 mM DTT, while there was no significant difference in the range of 20–100 mM DTT. (p<0.05) n=2, 10 mM; n=3 for 20, 50, 100 mM (Data from C. was also used in D.) E. Binding and elution of HEDJ from dTg does not depend upon free sulfhydryl groups in dTg. GdHCl denaturation included IA treatment that blocked sulfhydryl groups, making them unavailable for binding to HEDJ, whereas urea denaturation did not include IA. n=4 for each denaturant Values for F, E and B were not significantly different.