Figure 5.
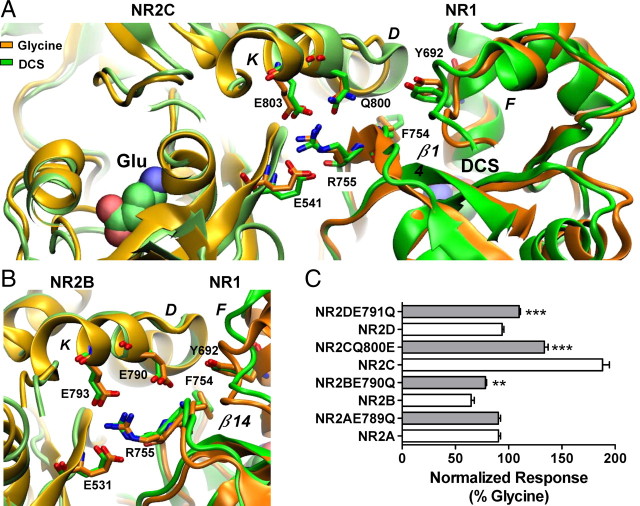
Residues at the dimer interface play a role in the control of the relative efficacy of DCS. A, Hydrogen bond formation between residues Arg755, Glu803 and Glu541 illustrating the dimer interface interaction, which correlates domain movement between the D2 domains of NR1 and NR2. Left, The NR2C subunit is colored lime and light orange for the DCS and glycine, respectively. Right, The NR1 subunit is colored green and orange with Arg755 protruding from the NR1–D2 domain interacting with Glu803 and Glu541 from the NR2C-D2 domain. The orientation change Phe754 undergoes between the DCS and glycine simulations can be observed on β-strand 14. Gln800 is shown protruding from helix K, no hydrogen bond formation with Tyr692 and Phe754 was observed. B, Hydrogen bond formation between residues Arg755, Glu793 and Glu531 illustrating the dimer interface interaction, which correlates movement between the D2 domains of NR1 and NR2. Left, The NR2B subunit is colored lime and light orange for the DCS and glycine, respectively. Right, The NR1 subunit is colored green (DCS) and orange (glycine) with Arg755 protruding from the NR1–D2 domain interacting with Glu793 and Glu531 from the NR2B-D2 domain. Glu790 protrudes from helix K to form hydrogen bonds with Tyr692 and the Phe754. C, Summary of changes in relative efficacy; efficacy between wild type and respective mutant receptors was compared by unpaired t test; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The fitted EC50 values are presented in Table 1.