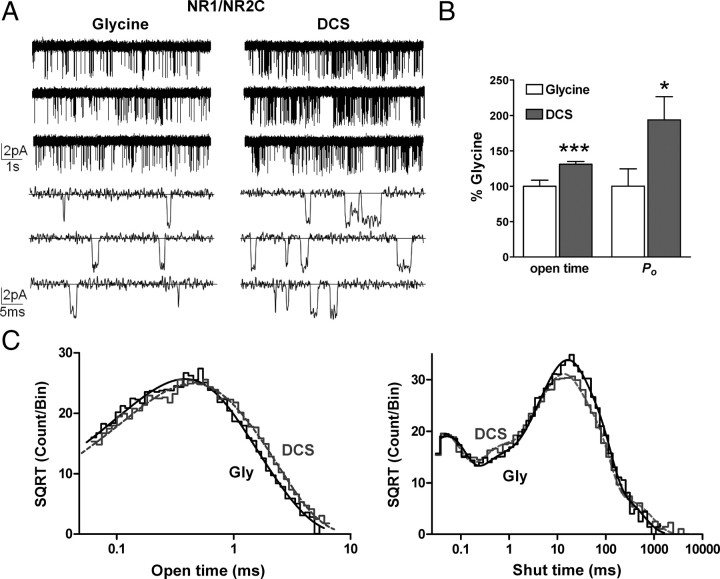
Figure 7.
DCS increases the mean open time and open probability of NR1/NR2C receptors. A, Steady-state recordings of NR1/NR2C unitary currents from an outside-out patch that contained one active channel in the presence of maximally effective concentration of glutamate and glycine or DCS (1 mm glutamate, 1 mm glycine or 1 mm DCS; VHOLD −80 mV, digitized at 40 kHz, filtered at 5–8 kHz, −3 dB) under two different time scales showing the increase in open probability and mean open time of the channel. B, Paired recordings in glycine and DCS in which we observed only one active channel were analyzed by time course fitting analysis using SCAN software (see Materials and Methods). The mean open time of NR1/NR2C receptors was increased by 131 ± 4% in the presence of DCS (n = 6, ***p < 0.001, paired t test). The open probability was increased by 194 ± 33% in the presence of DCS (n = 6, *p < 0.05, paired t test). C, The composite open time histogram from 6 patches was fitted by two exponential components [glycine: n = 6 patches, 11,275 open periods, τ1 = 0.32 ms (64%), τ2 = 0.68 ms (36%) and DCS: n = 6 patches, 16,662 open periods, τ1 = 0.32 ms (49%), τ2 = 0.76 ms (51%)]. The composite shut time histogram from 6 patches was fitted by five exponential components [glycine: n = 6 patches, 11,272 closed periods, τ1 = 0.042 ms (18%), τ2 = 0.36 ms (7%), τ3 = 9.1 (29%), τ4 = 32 ms (43%) and τ5 = 138 ms (3%) and DCS: n = 6 patches, 16,657 closed periods, τ1 = 0.037 ms (19%), τ2 = 0.48 ms (10%), τ3 = 9.5 ms (36%), τ4 = 36 ms (32%) and τ5 = 248 ms (3%)].