Figure 2.
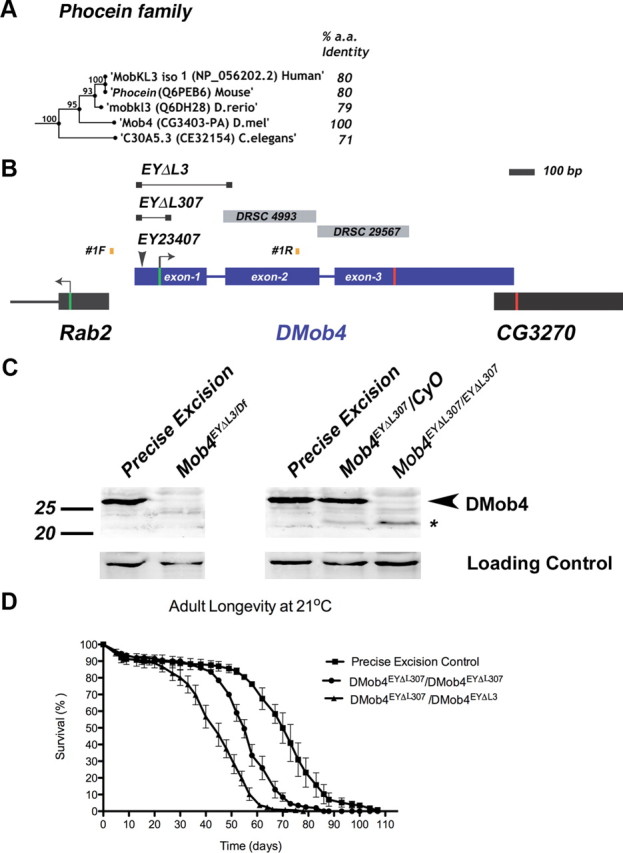
Molecular analysis of DMob4. A, Bootstrapping phylogenetic tree of the Phocein subfamily. The percentage amino acid conservation between DMob4 and Phocein proteins is noted to the right. Bootstrap scores are given at internodes. B, The DMob4 locus at band 42C5 on chromosome 2R is shown to scale. DMob4 (blue) has three exons (thick blue lines) that span ∼1.5 kb, including introns (thin blue lines). The ATG start codon is illustrated with a green bar in exon 1, whereas the stop codon is indicated with a red bar in exon 3. The breakpoints of the P-element excision mutants DMob4EYΔL3 and DMob4EYΔL307 are indicated (thin black lines with boxed ends). The insertion site of the progenitor P-element EY23407 is noted, as are the position of the oligonucleotides #1F and #1R used to identify excision mutants. Gray boxes DRSC4993 and DRSC29567 are dsRNA amplicons used for RNAi cell culture experiments. Rab2 and CG3270 flank the DMob4 locus. C, Western blot analysis of DMob4EYΔL3 and DMob4EYΔL307 excision mutants. The strain EYΔHV1223 was used as the precise excision control. Df refers to Df(2R)42, which is a small chromosomal deletion that spans the DMob4 locus. The expected molecular weight for DMob4 is 25.7 kDa. Dlg was used as a loading control. D, Adult longevity of the DMob4EYΔL307 hypomorphic excision mutant, DMob4EYΔL307/DMob4EYΔL3 transheterozygous deletions mutant, and precise excision control.
