Figure 7.
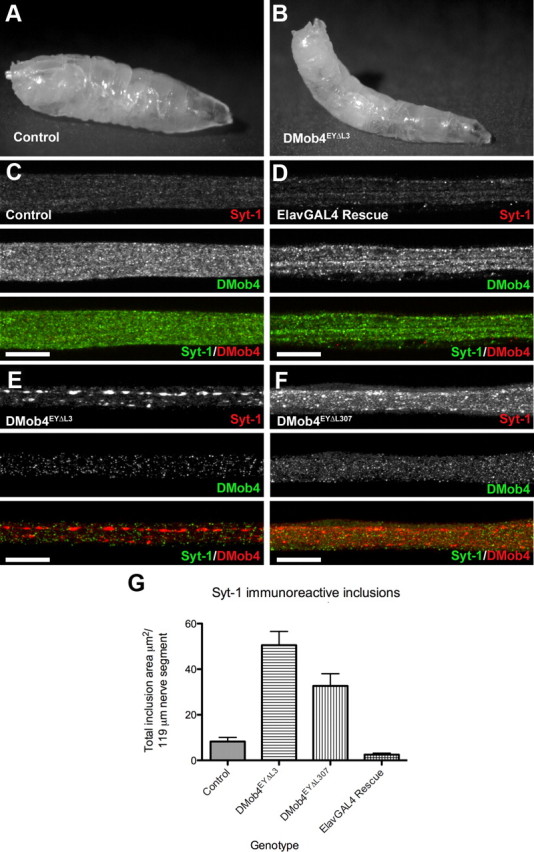
Axonal transport defects in DMob4 mutants. A, B, DMob4 mutant third-instar larvae have a tail-flip phenotype (B) compared with controls (A). C–F, Peripheral nerves of third-instar larvae coimmunolabeled for Syt-1 (red) and DMob4 (green). Blockade of axonal transport in DMob4EYΔL3/Df(2R)42 (null) and DMob4EYΔL307/Df(2R)42 (hypomorph) mutants results in accumulation of Syt-1 in large aggregates along the length of peripheral nerves (E, F). Axonal transport defects in DMob4EYΔL3 mutants can be rescued with the ectopic expression of UAS–DMob4 in neurons using the ElavGal4 driver (D). G, Quantification of Syt-1 immunoreactive inclusions present in peripheral nerves of DMob4 mutants, controls, and rescued animals. Scale bar, 20 μm.
