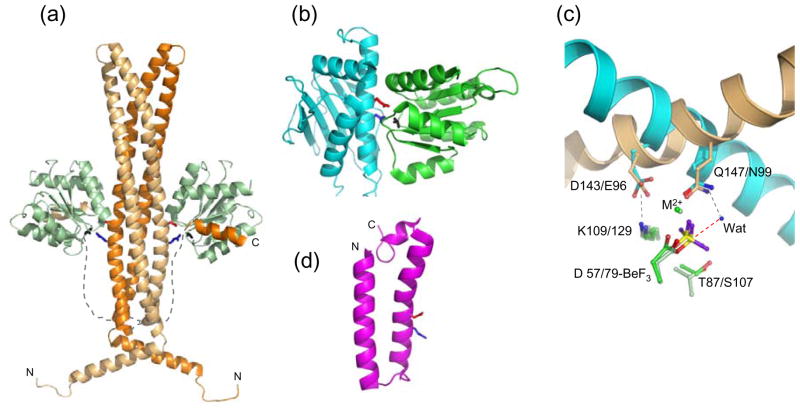
Figure 2.
Structures of response regulator phosphatases and their active sites. (a) The E. coli CheZ·CheY·BeF3−·Mg2+ complex (pdb 1KMI) with the two chains of the CheZ dimer as light orange and dark orange ribbons and the CheZ linkers sketched as dashed lines. CheY is in light green ribbons. The CheZ catalytic surface is defined by conserved acid (Asp143, red sticks) and amide (Gln147, blue sticks). BeF3− is in black sticks. (b) B. burgdorferi CheX·CheY·BeF3−·Mg2+ (pdb 3HZH) with CheX (cyan ribbon) and CheY3 (green ribbon). CheX conserved acid (Glu96, red) and amide (Asn99, blue) and BeF3− (black) are in stick representation. (c) Overlay of CheZ·CheY·BeF3−·Mg2+ and CheX·CheY3·BeF3−·Mg2+ active sites. The catalytic helices of CheZ (light orange) and CheX (cyan) are shown as ribbons and conserved CheX and CheZ residues are in sticks in the same color as the parent molecule. Select CheY residues are in sticks with E. coli CheY (light green) and B. burgdorferi CheY3 (green). BeF3− is yellow and purple. The ordered water molecule (‘Wat’) in the present CheX·CheY3·BeF3−· Mg2+ structure is a blue sphere and the red dashed line connects the water to the beryllium atom, the predicted path of nucleophilic attack. Interactions revealed in the crystal structures are gray dashed lines. (d) One of the 25 conformers in the NMR structure of B. anthracis BA5174 (pdb 2C0S), a member of the Spo0E family. The Gln (blue) and Asp (red) residues within the conserved (SQELD) motif are shown as sticks.