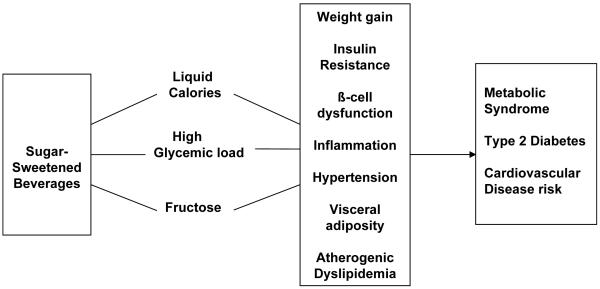
Figure 4. Potential biological mechanisms underlying the effect of SSBs on weight gain and risk of Metabolic Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Risk.
SSBs may lead to weight gain due to incomplete compensation for liquid calories at subsequent meals resulting in positive energy balance. Independent of weight gain, SSB’s may increase risk of MetSyn, T2DM and CVD due to their large contribution to a high dietary GL, and large fructose fraction, leading to development ofinsulin resistance, beta cell dysfunction, inflammation, hypertension, visceral adiposity and atherogenic dyslipidemia