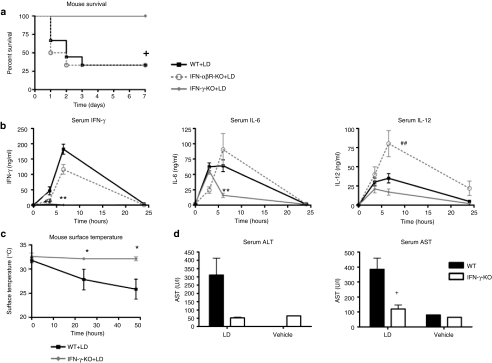
Figure 3.
IFN-γ played a key role in the innate immune response to liposome:DNA (LD) vector complex: experiments using genetic knockouts. (a) There was significant mortality in wild-type (WT) and IFN-αβR-KO mice following injection of LD, whereas all IFN-γ-KO mice survived. Graph shows survival fractions (Kaplan–Meier method), +P = 0.0487 by Logrank test. (b) Serum IFN-γ and IL-6 levels were significantly reduced in IFN-γ mice versus WT mice, and there was a trend toward reduced IL-12, after injection of LD. IL-6 and IL-12 levels were similar in IFN-αβR-KO mice and WT mice, whereas IL-12 levels were significantly higher in IFN-αβR-KO mice, after injection of LD. For all graphs P ≤ 0.0387 for 0- to 6-hour time points by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Bonferroni post-test **P < 0.01 for IFN-γ-KO versus WT. ##P < 0.01 for IFN-αβR-KO versus WT. (c) Surface body temperature dropped significantly in WT mice injected with LD, whereas IFN-γ-KO mice maintained normal temperature. P = 0.0033 by two-way ANOVA for 0- to 48-hour time points, Bonferroni post-test *P < 0.05 for IFN-γ-KO versus WT. (d) There was trend toward reduced serum ALT, and AST values were significantly lower in IFN-γ-KO mice versus WT mice at 24 hours after injection of LD. ALT and AST remained at background levels in mice injected with 5% dextrose vehicle. *P < 0.05 by t-test. (b–d) Graphs show mean ± SE. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; KO, knockout.