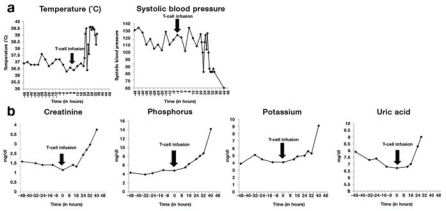
Figure 1.
Clinical assessment of subject 4 on IRB no. 06-138, NIH-RAC no. 0507-721, NCT00466531. Assessment of patient from the time of admission to the hospital before cyclophosphamide chemotherapy (–48 hours), through time of modified T-cell infusion (0 hours), to time of death (44 hours). Clinical status was assessed by routine vital sign parameters, including (a) temperature and systolic blood pressure, as well as by laboratory chemistry measurements, including (b) renal function as measured by creatinine, potassium, phosphorus, and uric acid concentrations. Vital signs over time are consistent with a sepsis syndrome (fever with hypotension), whereas laboratory chemistry studies demonstrate an initial rise in creatinine coinciding with the patient's anuric state, followed by rising potassium, phosphorus, and uric acid at concentrations that are consistent with tumor lysis but confounded by the antecedent acute renal failure. The vertical arrow indicates the time of T-cell infusion.